Fig. 2.
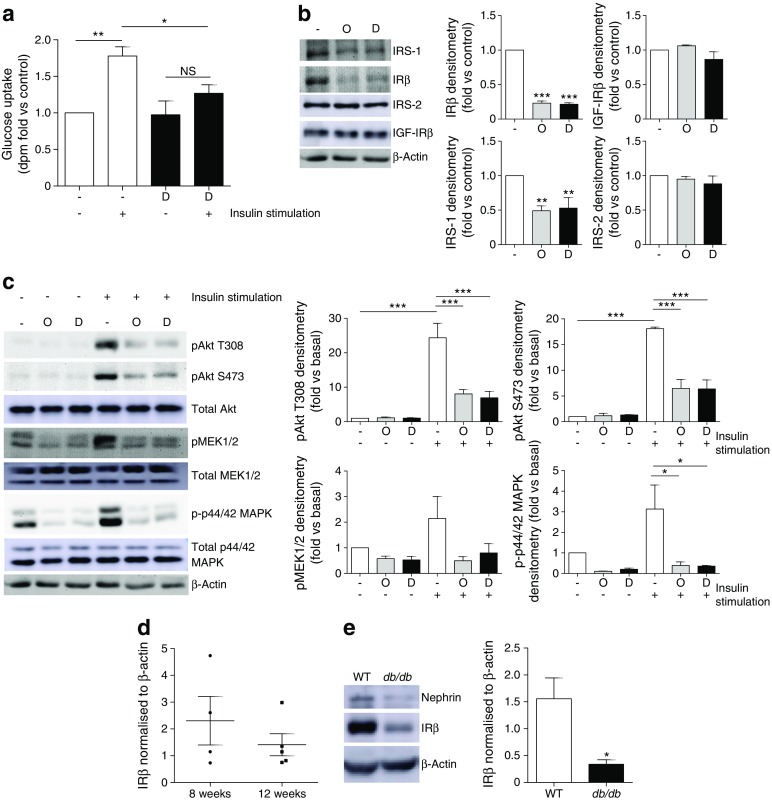
Loss of IRs in diabetic mouse podocytes in vitro and in glomeruli from db/db mice. WT mouse podocytes were treated for 10 days with 1 ng/ml TNF-α, 1 ng/ml IL-6, 100 nmol/l insulin and 25 mmol/l glucose (labelled Diabetic, D), prior to insulin stimulation (100 nmol/l). (a) dpm counts representing cellular uptake of [3H]2-deoxy-d-glucose following exposure of podocytes to the diabetic factors (D); n = 4. (b) Representative western blots and densitometry of IRS-1, IRβ, IRS-2 and IGF-IRβ protein following exposure of podocytes to the diabetic factors (D), or with mannitol (in parallel with insulin and inflammatory cytokines) included in place of glucose as an osmotic control (O); n = 4. (c) Representative western blots and densitometry of insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of Akt (T308, S473), mitogen-activated ERK-activating kinase (MEK1/2) and p44/42 MAPK (Thr202/Tyr204); n = 3. (d) IR protein in glomeruli isolated from db/db mice at 8 (n = 4, two males and two females) and 12 weeks (n = 5, three males and two females) of age. (e) IRβ protein in podocyte cultures isolated from 3-month-old db/db mice and WT littermate controls; n = 6. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparison
