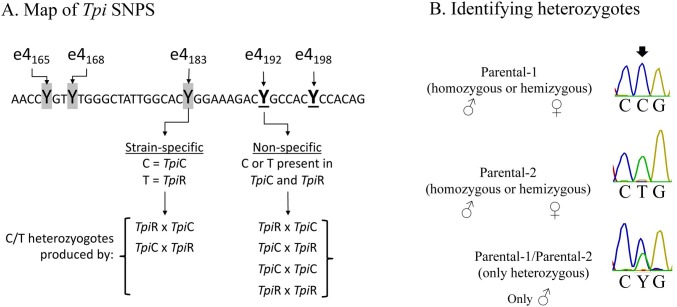
Fig 2. Map of selected Tpi SNPs that differ in strain-specificity including a list of the crosses that will produce heterozygotes at these sites and a description of the method to identify heterozygotes.
(A) DNA sequence of the segment of the fourth exon of the coding region containing three strain-specific sites (shaded) and two non-specific sites (underlined and bold). All SNPs are associated with a C or T (designated Y by IUPAC convention). Below are the types of crosses that can produce heterozygotes at e4183 and e4192. (B) Example of DNA sequencing chromatographs diagnostic of the two parental alleles as present as a hemizygote or homozygote, and the chromatograph representing the heterozygous combination that shows an overlap of the parental curves.