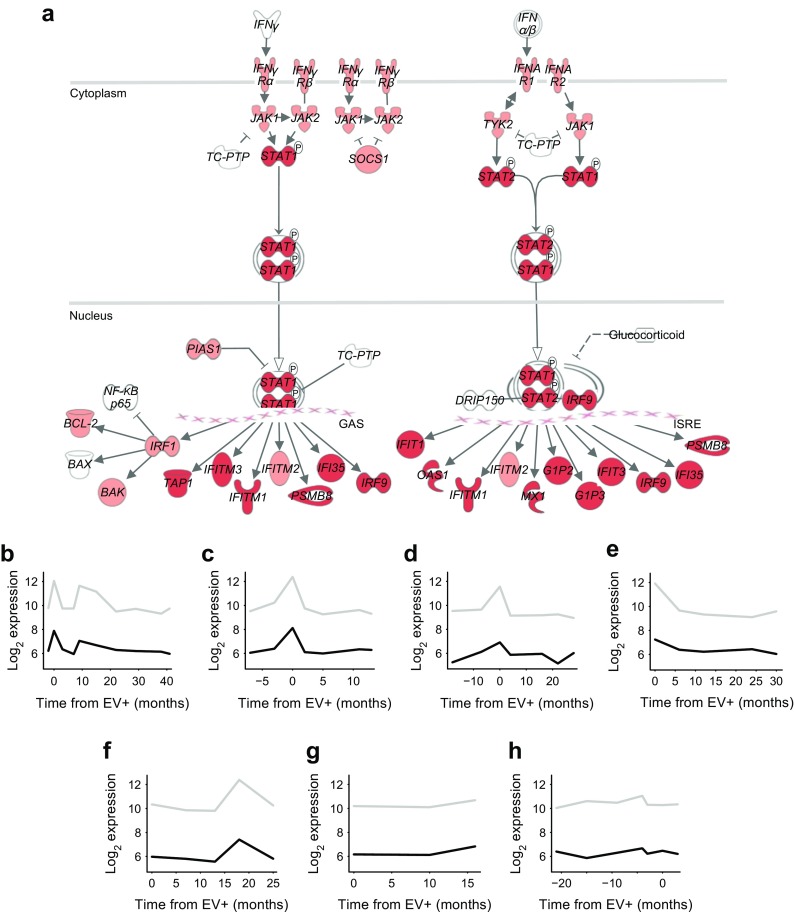
Fig. 2.
(a) Genes in peaking clusters mapping to the interferon signalling pathway based on the IPA tool. Red, genes present in at least four peaking clusters of the strongly enterovirus-positive children; pink, genes present in at least one peaking cluster. (b–h) Child-specific expression profiles of two genes of the interferon signalling pathway, MX1 (grey) and STAT2 (black). IFNγ is also known as IFNG; IFNα/β is also known as IFNA1/B1; TC-PTP is also known as PTPN2; NF-κB p65 is also known as RELA; BCL-2 is also known as BCL2; BAK is also known as BAK1; DRIP150 is also known as MED14; G1P2 is also known as ISG15; G1P3 is also known as IFI6. EV+, enterovirus-positive; GAS, IFNG-activated sequence; ISRE, interferon-stimulated regulatory element. The five children with strongly enterovirus-positive blood samples are denoted as Strong 1–Strong 5 (b–f). The two children with weakly enterovirus-positive blood samples are denoted as Weak 1 and Weak 2 (g, h)