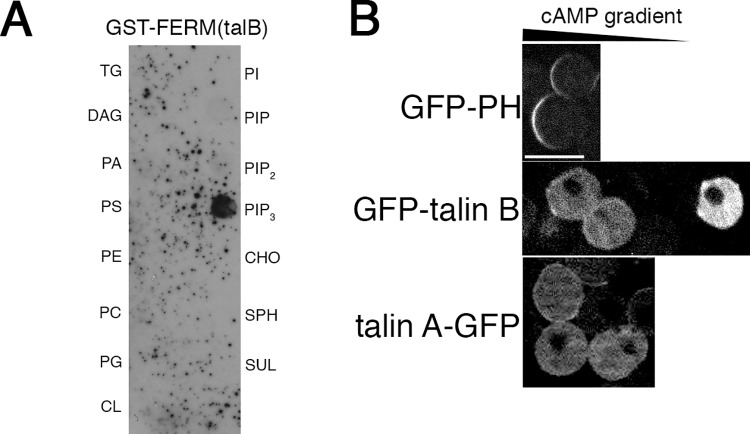
Fig 2. Biochemical properties of the talin B FERM domain and requirement of actin filaments for the talin B localization.
(A) Biochemical assay to determine the binding specificities of the FERM domain of talin B to the plasma membrane components. A bacterial lysate containing GST-FERM was reacted with a membrane strip spotted with 15 unique lipids. GST-FERM bound to the indicated lipids was immunologically detected. TG, triglyceride; DAG, diacylglycerol; PA, phosphatidic acid; PS, phosphatidylserine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; CL, cardiolipin; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PIP, PtdIns(4)P; PIP2, PtdIns(4,5)P2; PIP3, PtdIns(3,4,5)P3; CHO, cholesterol; SPH, sphingomyelin; and SUL, 3-sulfogalactosylceramide. (B) Sub-cellular localizations of the GFP-PH domain of CRAC, a probe for PtdIns(3,4,5)P3, as well as GFP-talin B and talin A-GFP, in the cAMP gradient after treatment of starved cells with latrunculin A. Scale bar: 10 μm.