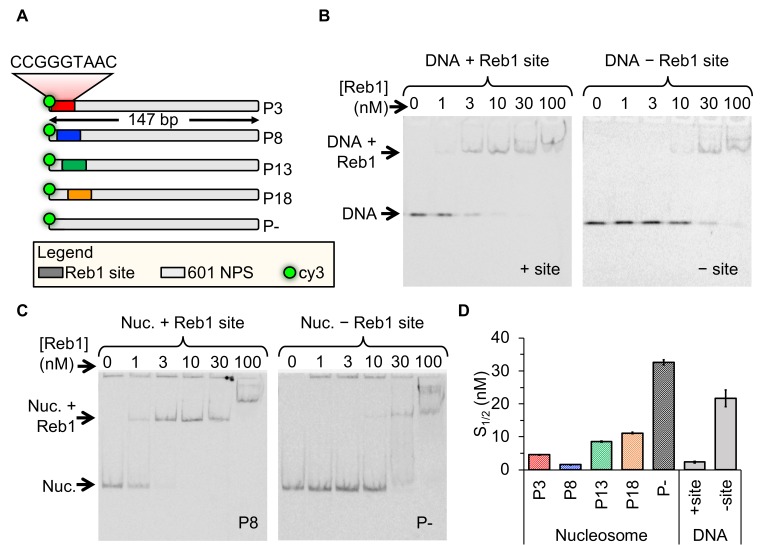
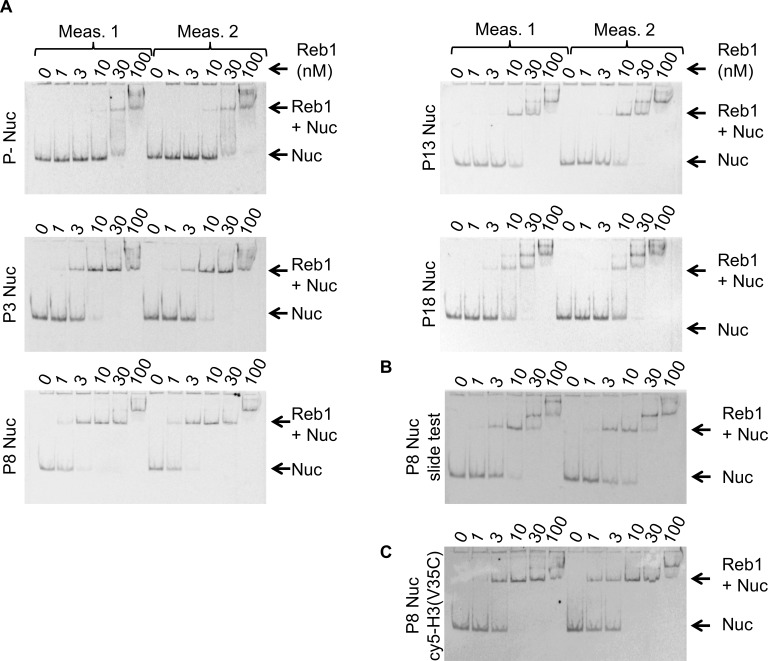
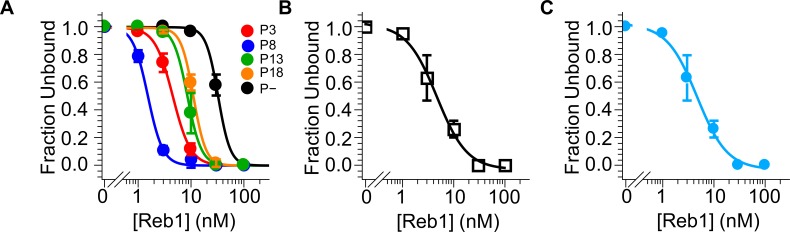
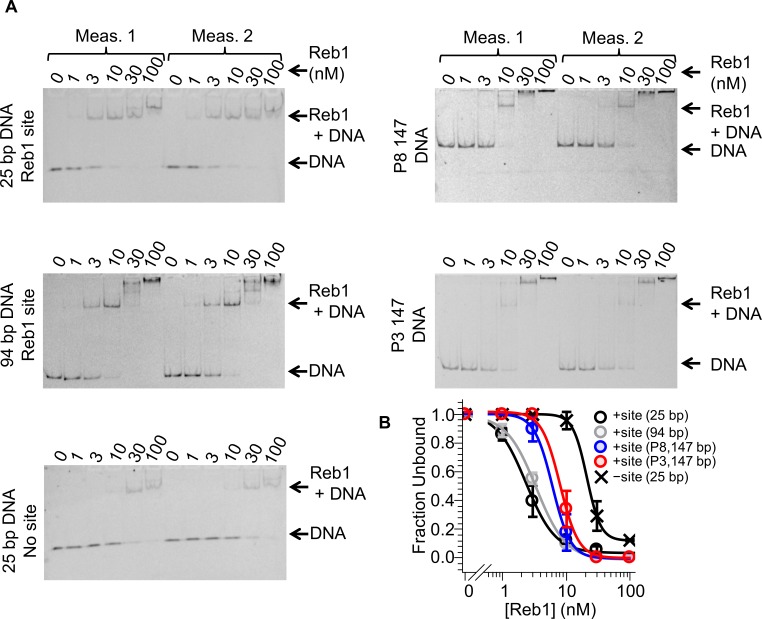
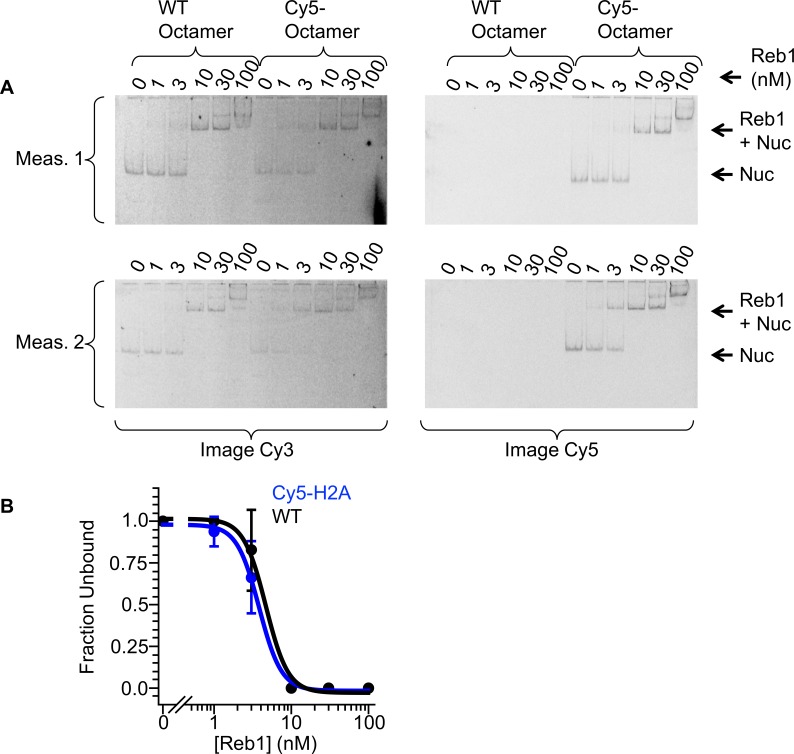
Figure 1. Reb1 binds DNA and nucleosomes with similar affinities.
(A) Design of the modified ‘601’ nucleosome positioning sequences (NPS) used in this study. Colored rectangles represent the Reb1-binding site at positions P3 (red), P8 (blue), P13 (green) and P18 (gold) within the 601 NPS. The numbers indicate the starting position of the Reb1-binding site (in number of base pairs into the 601 NPS). (B) Cy3 image of the EMSA of Reb1 binding to a 25-bp DNA sequence with (left) or without (right) the Reb1-binding site. (C) Cy5 image of the EMSA of Reb1 binding to P8 nucleosomes with (left) or without (right) the Reb1-binding site. (D) Quantification of the S1/2s determined from the Reb1 EMSAs in panels (B) and (C) and in Figure 1—figure supplement 3 (S1/2 Reb1–DNA + site EMSA = 2.3 ± 0.2 nM, S1/2 Reb1–DNA – site EMSA = 21.7 ± 2.3 nM, S1/2 Reb1–Nuc P3 EMSA = 4.6 ± 0.1 nM, S1/2 Reb1–Nuc P8 EMSA = 1.5 ± 0.1 nM, S1/2 Reb1–Nuc P13 EMSA = 8.5 ± 0.2 nM, S1/2 Reb1–Nuc P18 EMSA = 11.2 ± 0.3 nM, S1/2 Reb1–Nuc P – EMSA = 32.7 ± 0.8 nM). These results show that Reb1 binds nucleosomes and DNA sites specifically with a similar S1/2.