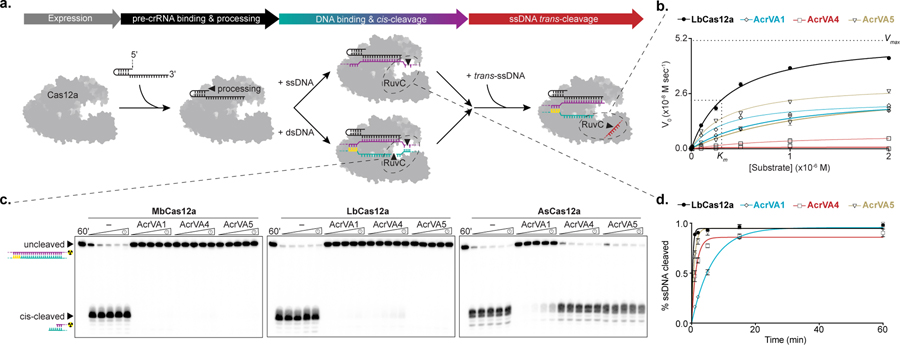
Figure 1 – AcrVAs do not inhibit all modes of DNA targeting by Cas12a.
a) Schematic representation of the steps in Cas12a target interference, b) Michaelis-Menten fit for 0.1 nM effective LbCas12a holoenzyme in the absence (black) or presence of AcrVA1 (blue), AcrVA4 (red), or AcrVA5 (yellow). The mean initial velocity (V0) is plotted against increasing DNase-Alert substrate concentrations (µM), where n = 3 replicates. The Vmax and Km for wild-type LbCas12a RuvC are indicated with dashed lines. c) Radiolabeled kinetic dsDNA cleavage assays for (left to right) MbCas12a, LbCas12a, and AsCas12a complexes with or without AcrVAs. Time courses represent 1’, 2’, 5’, 15’, and 60’. The uncleaved and cis-cleaved fractions are indicated with black triangles, d) Quantified percentage ssDNA cleaved for LbCas12a in the presence or absence of AcrVAs (mean ± sd, n = 3 independent experiments). Experimental fits are shown as solid lines and the calculated pseudo-first-order rate constants (kobs) (mean ± sd) are 2.6 ± 0.3 min−1, 0.15 ± 0.01 min−1, 0.7 ± 0.06 min−1, and 1.2 ± 0.09 min−1 for LbCas12a, LbCas12a+AcrVA1, LbCas12a+AcrVA4, and LbCas12a+AcrVA5 respectively. Source data for panels b and d are available with the paper online. The uncropped gel images are available in Supplementary Data Set 1.