Figure 8: Alcohol-associated intestinal dysbiosis increases host susceptibility to Streptococcus pneumoniae in mice, independent of alcohol or HIV infection.
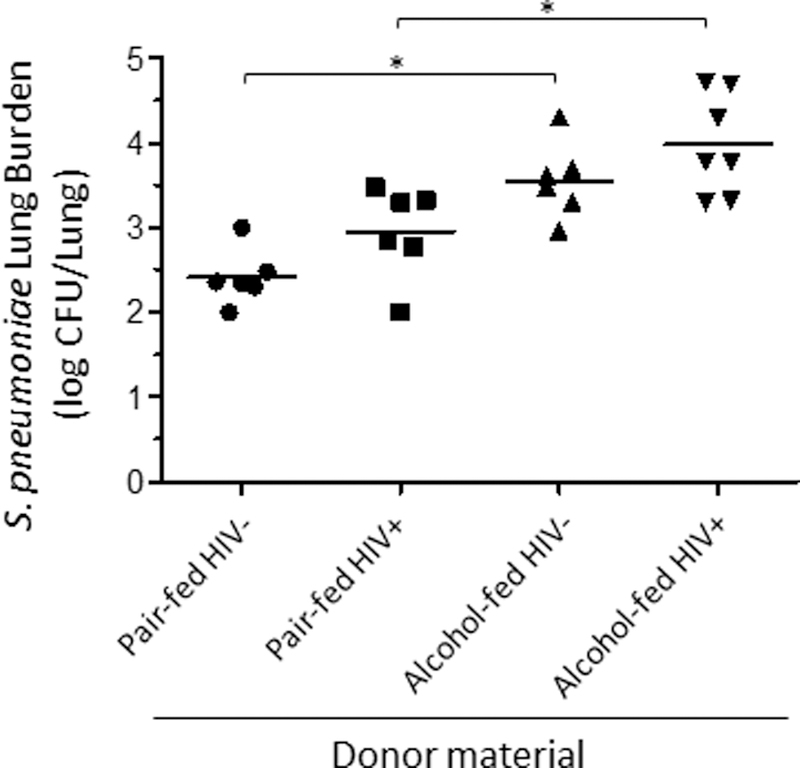
Streptococcus lung burden (Log10 CFU/ml) at 48 hrs. post infection in animals recolonized with microbiota from HIV+ ethanol-fed, HIV+ pair-fed, HIV- ethanol-fed, or HIV- pair-fed. Bars represent the median log10 CFU/lung of S. pneumoniae. * indicates P < 0.05, by Mann-Whitney U or by ANOVA with Dunn’s correction. N=10/group.
