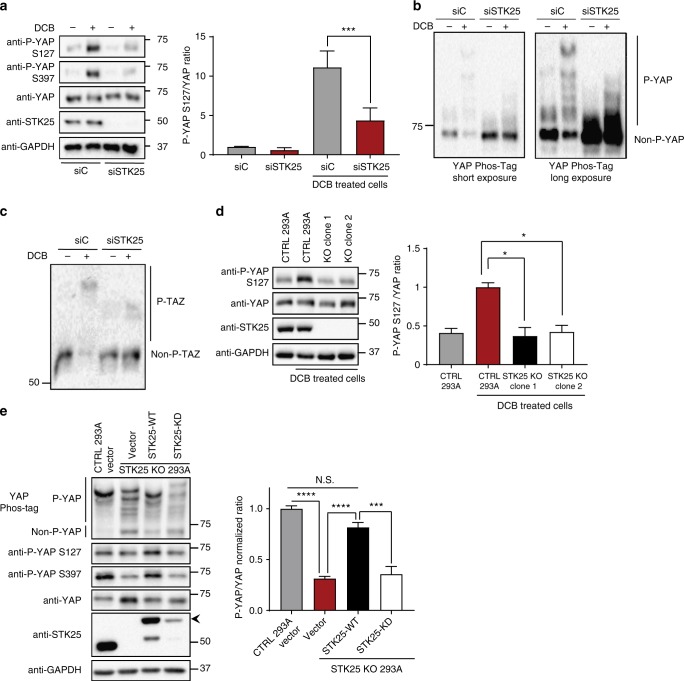
Fig. 1.
STK25 regulates Hippo activation in response to loss of cytoskeletal tension. a Immunoblot and quantitation of phosphorylated YAP levels following treatment with 10 µM DCB in HEK293A cells transfected with the indicated siRNA (n = 6; ***p < 0.001, unpaired t-test). b Global phosphorylation status of YAP was assessed using Phos-tag gel electrophoresis following treatment with 10 µM DCB in HEK293A cells transfected with either control siRNA or STK25 siRNA. Shifted bands indicate degrees of YAP phosphorylation. c TAZ phosphorylation status was assessed using Phos-tag gel electrophoresis following treatment with 10 µM DCB in HEK293A cells transfected with either control siRNA or STK25 siRNA. d Immunoblot and quantitation of phosphorylated YAP levels following treatment with 10 µM DCB in either control HEK293A stably expressing Cas9 and a non-targeting sgRNA or STK25 KO 293A stably expressing Cas9 together with either sgRNA 1 (Clone 1) or sgRNA 2 (Clone 2) targeting STK25 (n = 4; *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc analysis). e Immunoblot and quantitation of phosphorylated YAP levels in control 293A cells and STK25 KO 293A cells transfected with either Vector, Cas9-resistant FLAG-STK25-WT, or Cas9-resistant FLAG-STK25-KD. Global levels of YAP phosphorylation in these samples were also assessed using Phos-tag gel electrophoresis. Quantitation corresponds to levels of phosphorylated YAP as measured via phos-tag electrophoresis (n = 4; ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc analysis). All data are presented as mean ± SEM