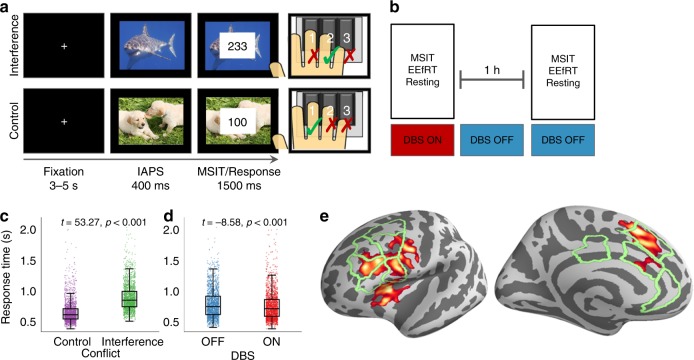
Fig. 1.
Experiment design and behavior. a Affective multi-source interference task (MSIT). Subjects chose the number that differed from its neighbors while ignoring an emotionally arousing image. On interference trials (top), a non-intuitive motor mapping and flanking distractors increased cognitive load. b Subjects performed task and resting recordings with deep brain stimulation (DBS) ON and again after 60 + minutes with DBS OFF. c Interference increased response times (RTs) (n = 3785 trials from 14 subjects, t = 53.3, p < 1e–20, Wald test of generalized linear model (GLM) coefficient). d DBS reduced RTs by 34 ms (t = −8.6, p < 1.33e–17). Error bars represent standard error of the mean. e Atlas labels for source localization overlaid on functional MRI interference/control contrast from past studies