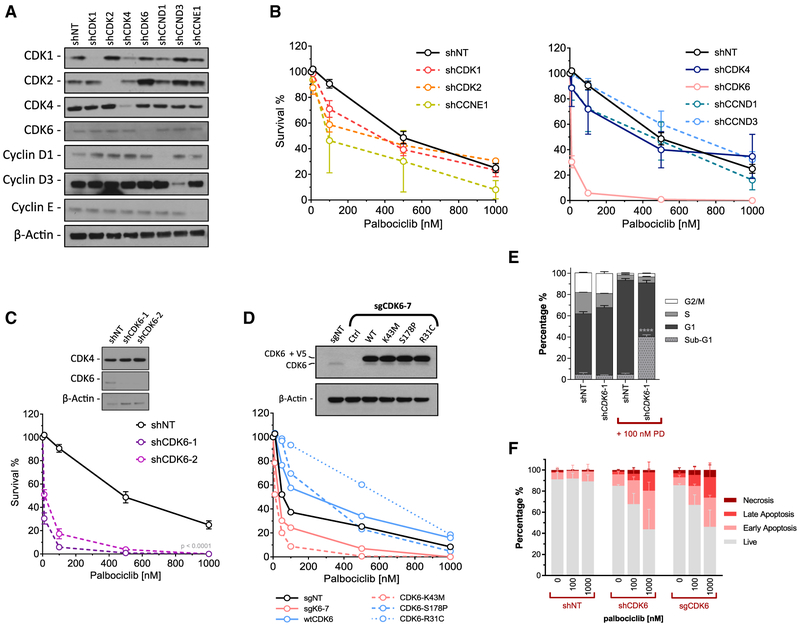
Figure 3. CDK6 Expression and Activity Contributes to Cell Survival after Palbociclib Exposure.
(A) Western blot analysis of shRNA-mediated knockdown of cell-cycle proteins in T47D cells.
(B) Clonogenic survival assay after 24 h of palbociclib exposure on shRNA-expressing T47D cells. Data are reported as the means ± SEMs of 3 independent experiments.
(C) Confirmatory CDK6 knockdown and clonogenic survival assay with an additional CDK6 shRNA. Survival was significantly decreased in both shCDK6-1 and -2 compared to shNT (p < 0.0001). Data are reported as the means ± SEMs of 3 independent experiments.
(D) Western blot of T47D cells with CRISPR/Cas9 knockout of CDK6 using an sgRNA targeting the 5′ UTR, followed by ectopic expression of CDK6 mutants. Clonogenic survival assay of CRISPR/Cas9 knockout CDK6, and mutant add-back lines treated with escalating dose of palbociclib.
(E) Cell-cycle analysis of shCDK6 T47D cells ± 100 nM palbociclib treatment for 24 h. Data are reported as the means ± SEMs of 3 independent experiments. ****p < 0.0001.
(F) Annexin V apoptosis assay using shSCR, shCDK6, and sgCDK6 T47D cells treated with escalating doses of palbociclib for 48 h. Data are reported as the means ± SDs of 2 independent experiments.