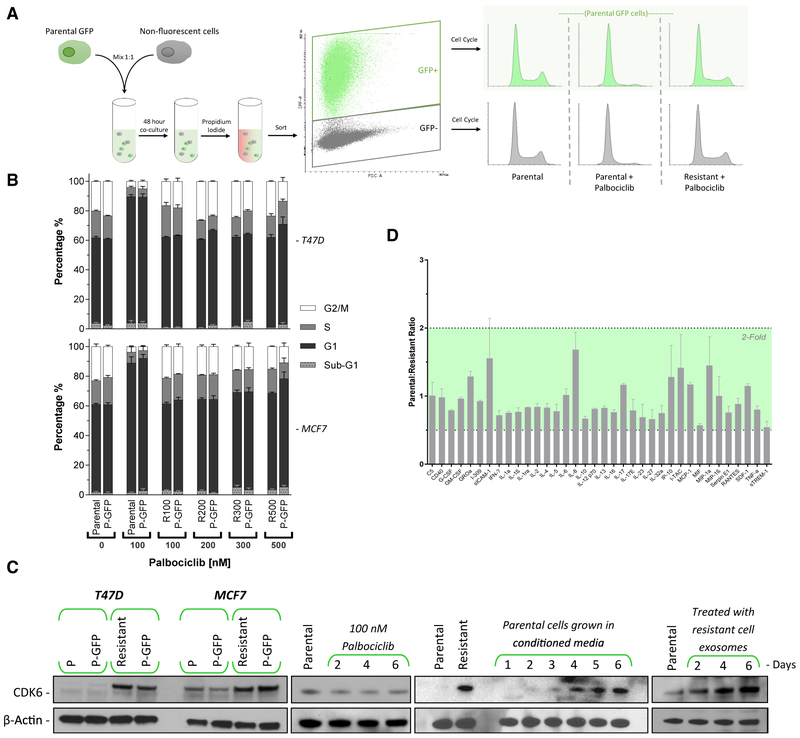
Figure 4. CDK4/6 Inhibitor Resistance Is Transmitted via Exosomal Signaling.
(A) A schematic representation of the assay to test resistance transmission from a resistant cell to a non-resistant population. Parental cells were engineered to express GFP and mixed with non-fluorescent parental or resistant cells and incubated for 48 h. Cells were then sorted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) based on GFP status, and the cell-cycle profiles of both GFP+ and GFP− populations were analyzed.
(B) Cell-cycle analysis of parental, GFP+ T47D, and MCF7 cells co-cultured for 96 h with palbociclib-resistant (100–500 nM) cells. Adjacent bars represent cells that were co-cultured. The palbociclib concentration in the medium was maintained at the level of the resistant cells. Data are reported as the means ± SEMs of 3 independent experiments.
(C) Western blot analysis of CDK6 protein expression. Panel 1: parental GFP cells were co-cultured with either parental or resistant cells for 48 h, then FACS sorted by GFP expression. Panel 2: T47D cells were treated with palbociclib for up to 6 days. Panel 3: parental T47D cells were incubated with conditioned medium from resistant cells. The medium contained 100 nM palbociclib and was replaced daily. Panel 4: exosomes from resistant T47D cell medium were harvested and subsequently added to parental cells daily for 6 days.
(D) Excreted cytokine assay performed on conditioned medium from resistant versus parental cell T47D cells. Data are reported as the means ± SDs cytokine expression of 2 independent experiments.