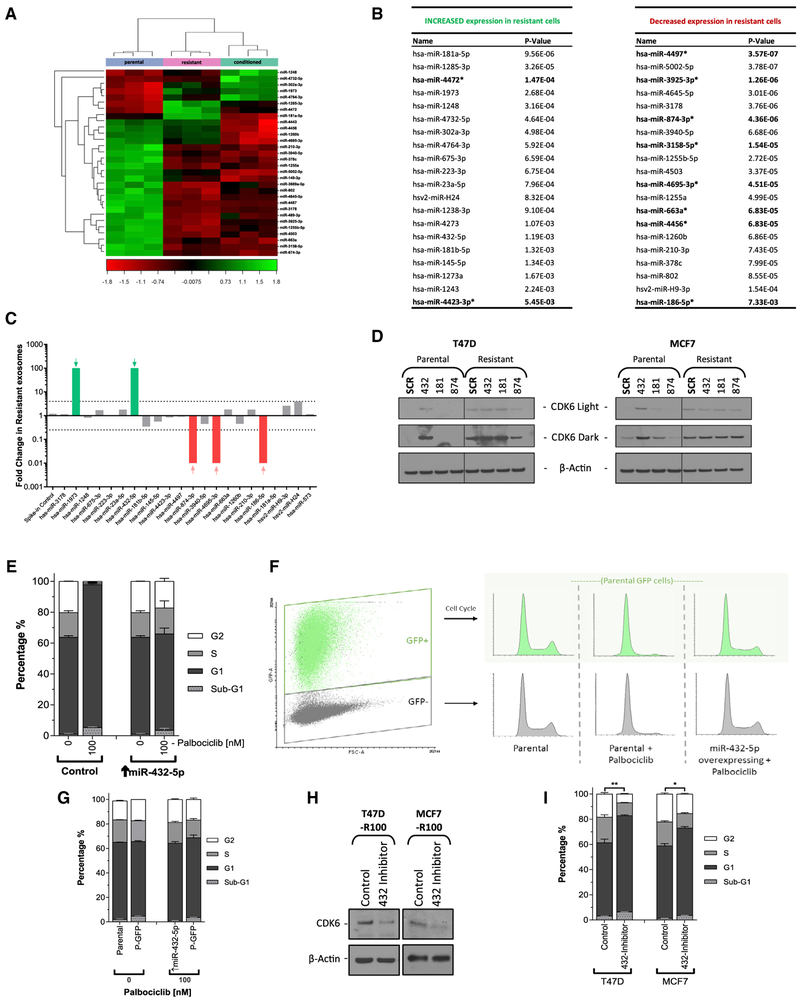
Figure 5. Resistance Is Mediated by Exosomal miR-432-5p.
(A) Hierarchal clustering of 30 miRNAs from miRNA expression profiling that display large-magnitude changes between parental, resistant, and parental T47D cells treated for 48 h with resistant cell medium.
(B) Significantly changed miRNAs grouped by expression in resistant relative to parental cells, sorted by significance. Highlighted miRNAs are significantly predicted to target CDK6 mRNA.
(C) Exosomes were harvested from the media of parental and resistant T47D cells. Real-time qPCR was performed to detect each of the miRNAs listed previously. The expression of detectable miRNAs is presented as fold change in resistant versus parental exosomes.
(D) Western blot analysis of CDK6 protein in resistant and parental T47D and MCF7 cells overexpressing selected miRNAs.
(E) Cell-cycle analysis of parental and miR-432-5p overexpressing T47D cells ± 100 nM palbociclib. Data are reported as the means ± SEMs of 3 independent experiments.
(F and G) GFP+ parental T47D cells were co-cultured for 48 h with either parental or miR-432-5p overexpressing cells (↑miR-432-5p) ± 100 nM palbociclib. Cells were then flow sorted by GFP status and analyzed for cell-cycle distribution (F). Data are reported as the means ± SEMs of 3 independent experiments (G).
(H and I) Resistant T47D and MCF7 (R100) cells were transfected with an miR-432-5p inhibitor and then incubated for 96 h before being analyzed by western blot (H) to determine CDK6 protein levels or by flow cytometry (I) to determine the cell-cycle distribution. Data are reported as the means ± SEMs of 3 independent experiments.