Figure 4.
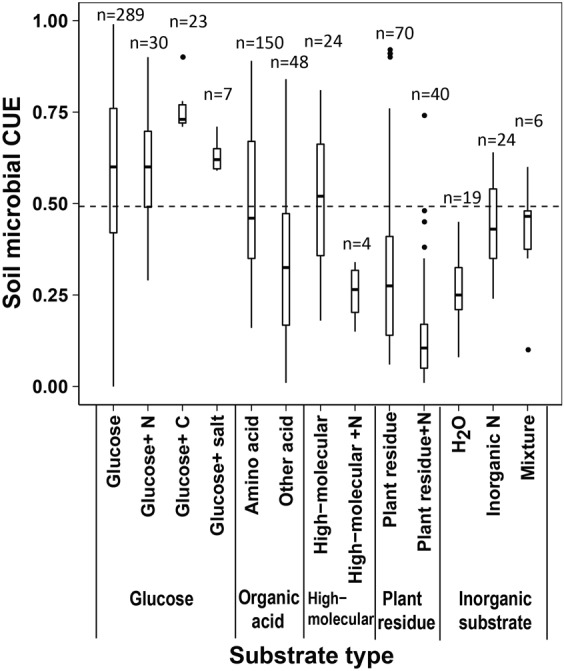
The mean CUE of main five different substrate types. (1) The substrate of glucose including glucose, sugar with inorganic N (glucose + N), glucose with other organic C (glucose + C), and glucose with inorganic salt (glucose + salt); (2) the substrate of organic acid dividing into amino acid and other acid; (3) The substrate of high-molecular including high-molecular substrate (protein, cellulose, cellobiose, plant cell walls, microbial cell walls, tri-palmitoyl-glycerol synthesis, polyhydroxybutyrate synthesis), high-molecular with inorganic N (high-molecular + N); (4) the substrate of plant residue including plant residue (a whole plant residue or plant parts (roots, leaves, stems)), plant residue with inorganic N (residue + N); (5) inorganic substrate dividing into H2O, inorganic N and the mixture.
