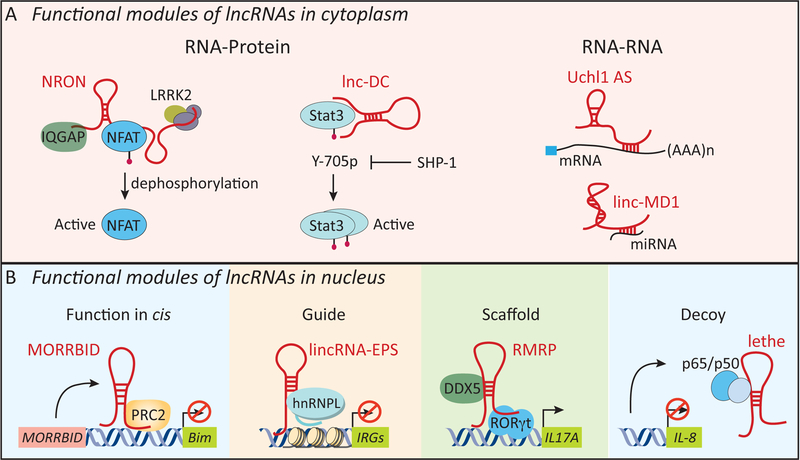
Figure 4. Mechanism of action for lncRNAs.
lncRNAs mediate their molecular functions through a multitude of mechanisms in cytoplasm (A) or the nucleus (B). In the cytoplasm, lncRNAs act through RNA-protein (e.g. NRON and lnc-DC) or RNA-RNA (e.g. Uchl1 AS and linc-MD1) interactions. NRON and lnc-DC act as molecular scaffolds for the transcription factors, NFAT and STAT3. Uchl1 AS interacts with target mRNAs through base-paring to enhance their translation. In the nucleus, lncRNAs can act in cis or trans (B). Morrbid interacts with PRC2 to repress the transcription of the neighboring gene, Bim (Bcl2l11), in cis in short-lived myeloid cells such as neutrophils and monocytes. lncRNAs can interact with their protein partners as guide (e.g. lincRNA-EPS: hnRNPL), scaffold (e.g. RMRP interaction with DDX5 and RORγt) or a decoy molecule (e.g. Lethe: NF-κB p65) to mediate their molecular functions. Uchl1, ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1; lMD1: muscle differentiation 1.