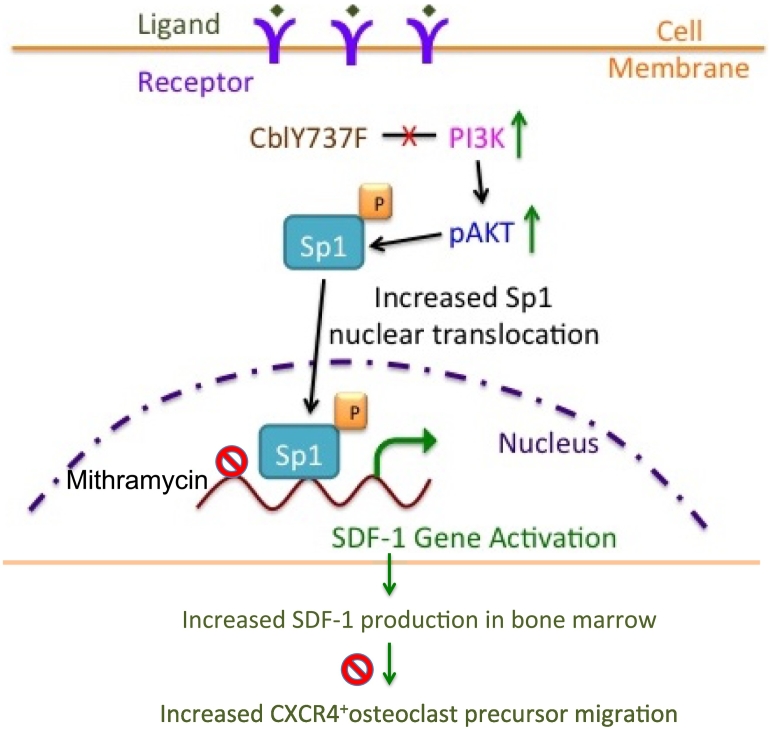
Fig. 6.
Proposed model depicting the role of PI3K/AKT/Sp1 axis on SDF-1 expression in CAR cells and the effect of increased SDF-1 levels on osteoclast precursor migration in response to increased PI3K activation. Loss of Cbl-PI3K interaction results in increased PI3K activity, which leads to increased phosphorylation of AKT. Sp1, an important substrate of PI3K is activated, translocated to the nucleus and binds to the SDF-1 promoter regions to activate SDF-1 transcription in CAR cells. Sp1 binding to SDF-1 promoter regions is inhibited by Mithramycin treatment resulting in decreased SDF-1 transcription to a lesser extent in YF cells compared to wild type cells due to increased Sp1 activation in YF cells. Increased SDF-1 gene expression leads to increased SDF-1 protein levels, which stimulate migration of osteoclast precursors expressing SDF-1 receptor, CXCR4. AMD3100 blocks CXCR4 activation by SDF-1 and prevents osteoclast precursor migration, to a lesser extent in YF cells compared to wild type cells. Increased osteoclast precursor migration might lead to increased recruitment to the bone marrow milieu finally contributing to increased number of osteoclasts in YF mice lacking Cbl-PI3K interaction.