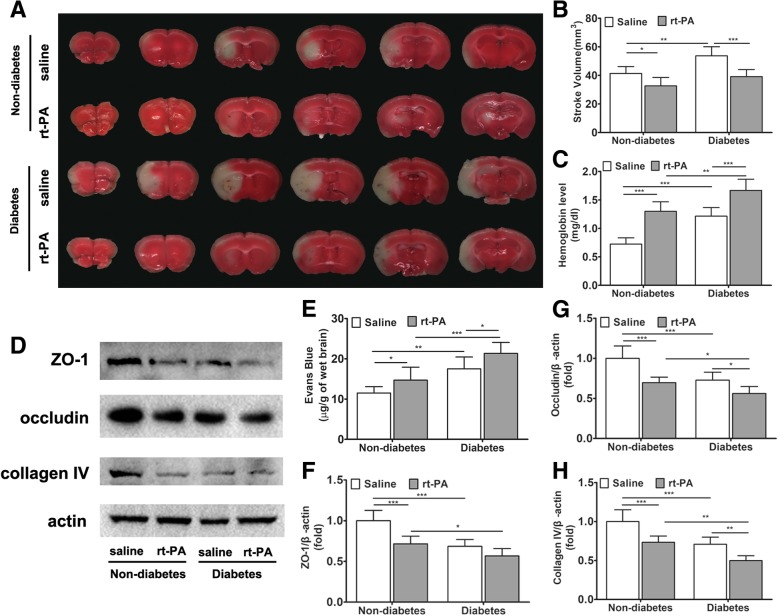
Fig. 1.
Diabetes increases HT and BBB disruption after rt-PA treatment of cerebral ischemia. Diabetes was induced in rats with streptozotocin. Cerebral Ischemia was induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion and treated with rt-PA or saline as control. Analysis was performed 72 h after ischemic attack. a Representative TTC staining images of four groups. b Stroke volume evaluated by TTC staining (n = 6 in each group). c Cerebral hemorrhage evaluated by spectrophotometric hemoglobin assay (n = 6 in each group). d Representative immunoblots of tight junction proteins zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) and occludin and collagen IV for each group. e BBB permeability assay with Evans blue dye (n = 10 in non-diabetic groups, n = 6 in diabetic groups). f–h Protein amounts were quantified from immunoblots and normalized to β-actin amount. Data expressed as mean ± SD and analyzed by two-way ANOVA. One asterisk (*) represents P < 0.05, two (**) P < 0.01, and three (***) P < 0.001. rt-PA recombinant tissue plasminogen activator, BBB blood-brain barrier, HT hemorrhagic transformation, TTC 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride, ZO-1 zonula occludens-1