Fig. 1.
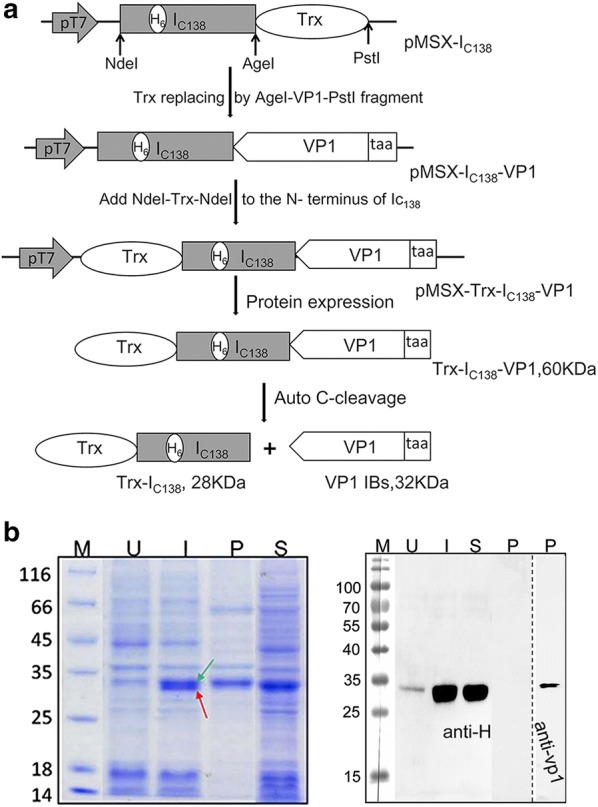
Schematic illustration of plasmid constructions and intein spontaneous C-cleavage assay in vivo. a Plasmid pMSX-IC138-VP1 was derived from previously described plasmid pMSX-IC138T [45] by replacing the Trx coding sequence with a VP1 sequence. Plasmid pMSX-Trx-IC138-VP1 was derived from plasmid pMSX-IC138-VP1 by adding a Trx fragment to the N terminus of IC138 gene sequence. The recombinant fusion protein Trx-IC138-VP1 consisted of Trx, Ic138 and VP1, with Trx being a thioredoxin protein, Ic138 being the 138-aa C-terminal part of the Ssp DnaX mini-intein, and VP1 being the Coxsackievirus B3 capsid protein-1. The Ic138 contained a 6xHis-tag (H6) as indicated. Spontaneous C-cleavage at the C-terminus of Ic138 would produce the two protein products as illustrated. b SDS–PAGE (left) and Western blotting (right) analysis of the C-cleavage of recombinant protein Trx-Ic138-VP1. Lane M: protein size markers, with their sizes shown in kDa. Lanes U and I: total cellular proteins of E. coli before and after IPTG-induced expression the Trx-Ic138-VP1 protein, respectively. Lanes P and S: the pellets and supernatants of the bacterial cell lysate after sonication, respectively. Predicted sizes of Trx-Ic138-VP1, Trx-Ic138 and VP1 are 60 kDa, 28 kDa and 32 kDa, respectively
