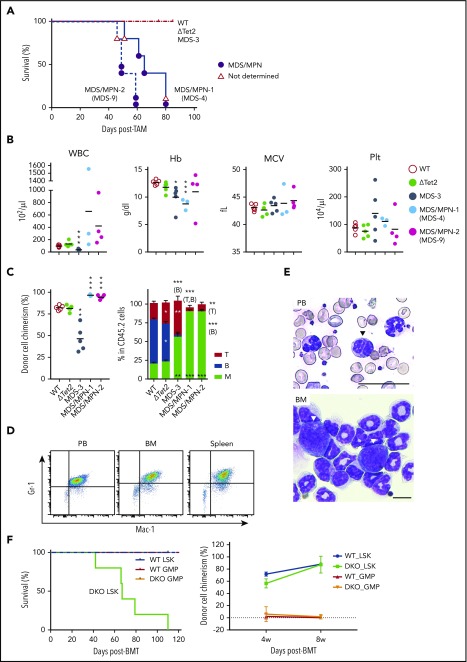
Figure 5.
ΔTet2ΔE9-10 MDS cells evolve into MDS/MPN during serial transplantation. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of recipient mice infused with BM cells from MDS-3, MDS-4, and MDS-9 mice and their WT and ΔTet2 control mice (n = 5 each). The causes of death in DKO mice are indicated by circles or triangles with different colors. (B) PB cell counts in recipient mice 3 months after transplantation (n = 3-5 each). (C) The chimerism of CD45.2 donor cells in PB 3 months after transplantation (n = 3-5 each). The proportions of myeloid (My) (Mac-1+ and/or Gr-1+), B220+ B cells, and CD4+ or CD8+ T cells among CD45.2+ donor-derived hematopoietic cells in PB are depicted in the right panels (n = 3-5 each). Data are shown as the mean ± SEM. Statistical significance is shown relative to WT. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001 by the Student t test. (D) MDS/MPN developed in recipients infused with BM from MDS-4 mice. Flow cytometric profiles of MDS/MPN cells in PB, BM, and the spleen. (E) Smear preparation of PB and cytospin preparation from moribund MDS/MPN (MDS-4) mice after May-Giemsa staining. Hyposegmented neutrophils consistent with a pseudo Pelger-Huët anomaly (arrowhead) in PB and scattered blasts (arrowheads) in BM are shown. Bars represent 50 and 10 μm, respectively. (F) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of recipient mice infused with LSK cells (1.2 × 104/mouse, n = 5 each) or GMPs (WT, 1 × 105 to 2 × 105 GMPs per mouse, n = 4; DKO, 2 × 105 GMPs per mouse, n = 5) from WT and DKO MDS mice (CD45.2+). Purified LSK cells and GMPs were transplanted into recipient mice sublethally irradiated at a dose of 6.5 Gy. The chimerism of CD45.2 donor cells in PB after transplantation is indicated in the right panel. MPN, myeloproliferative neoplasms.