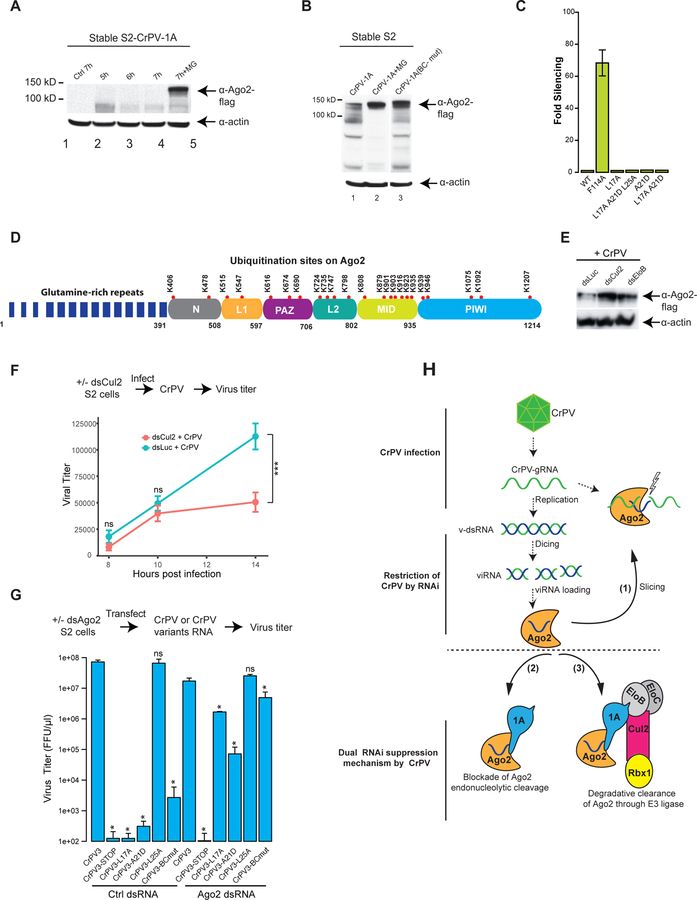
Fig 7: CrPV-1A-hijacked E3 ligase contributes to virus replication.
(A, B) The stability of Ago-2 in CrPV-1A or CrPV-1A(BC-mut) expressing S2 cells at indicated time points (h) in the presence or absence of MG132 was visualized by Western blot. A lane between 2 and 3 as shown in Fig B has been removed from the original blot for clarity. Western blots analysis are representative of three independent experiments (n = 3) (C) Effects of a single point or combined mutations in the BC-box of the CrPV-1A on RNAi suppression using the RNAi reporter assay. RNAi suppression data represent mean (±SD) of at least three independent experiments (n = 3) for each condition. (D) Red dots represent the ubiquitin sites on Ago-2 derived from S2 cells or S2 cells expressing CrPV-1A protein by UbiScan analysis. The Ubiquitin sites reported are representative of three independent experiments (n = 3). Approximate boundaries of the domains in Drosophila Ago-2 were derived from homology-based modeling using the structure of human Ago-2. (E) S2 cells expressing Ago-2-flag were depleted for Cul2 and EloB followed by infection with CrPV at MOI of 2. Twenty hours post infection, Ago-2 expression in S2 cells and loading controls were analyzed by Western blot using flag and actin antibodies, respectively. Western blots analysis is representative of two independent experiments (n = 2). (F) Cul2-depleted (dsCul2) or Luc-depleted (dsLuc) S2 cells were monitored by infection of CrPV at MOI of 2, and viral titer was measured by FFU assay. Data shows one of three representative experiments with the mean (±SD) of three replicates (n = 3). *p<0.05; ***p<0.001 (Multiple t test). (G) Ago-2-depleted S2 cells were transfected with CrPV3 RNA or CrPV3 variant RNA and viral titer was measured by FFU assay. Each titer value represents the mean (±SD) of at least three replicate experiments (n = 3). The statistical significance represents measurement compared to CrPV3. ns, not significant; *p<0.05 (Unpaired t test) (H) A model showing the mechanism of immune restriction against CrPV (top) and the mechanism deployed by CrPV to counteract this host immune response (bottom) in Drosophila cells.