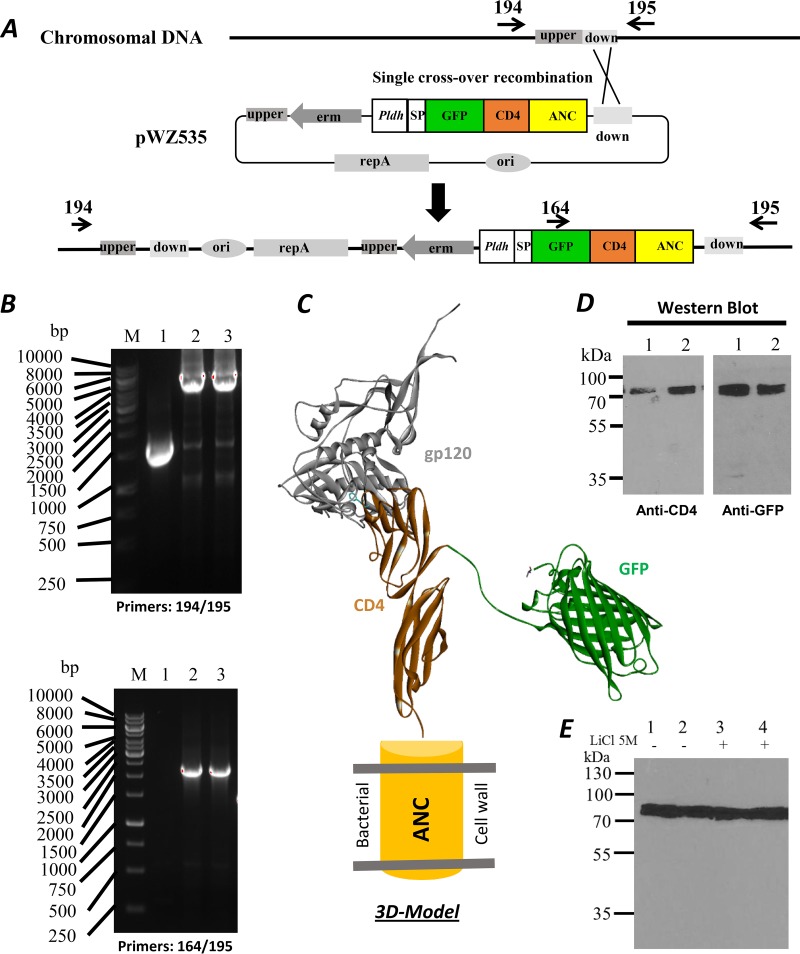
FIG 2.
Engineering of chromosomal integration for surface display. (A) Construction maps for chromosomal integration. The location of the down homologous sequence region was marked between the primers 194 and 195. (B) The DNA agarose gels showing PCR-amplified DNA fragments from the integrated L. acidophilus strain; 1, wild-type strain and 2 and 3 from two positive colonies; upper gel with the primers 194 and 195, lower gel with the primers 164 and 195. (C) 3D model of fusion surface display. The model was derived from crystal structures of the HIV-1 gp120-CD4 complex (PDB 3JWD) (42) and GFP (PDB 1GFL) (43). (D) Western blots with anti-CD4 and anti-GFP antibodies of the fusion protein in L. acidophilus. (E) Western blot showing the presence of the GFP-CD4 fusion protein after a 5 M LiCl wash. The GFP-CD4 fusion protein could not be removed from the cell by a 5 M LiCl wash. Members of the anchored family of surface proteins can only be released by enzymatic degradation of peptidoglycan.