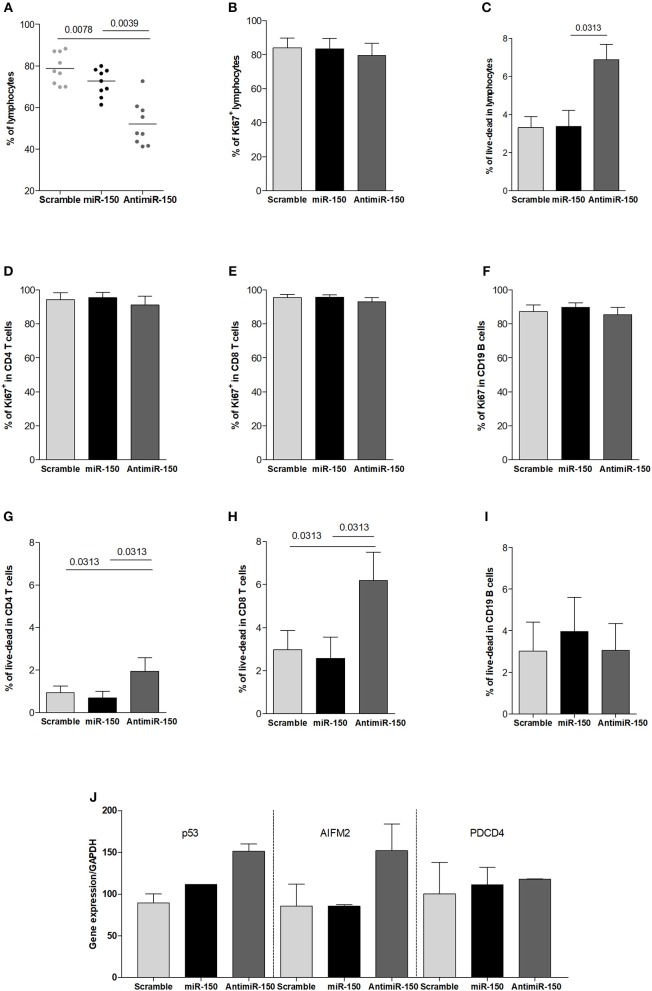
Figure 5.
Increased cell death due to miR-150 inhibition. (A) Analysis of the effect of miR-150 and antimiR-150 on the percentage of lymphocytes. PBMCs from 9 control donors were cultured for 72 h with a scramble miRNA (10 μM), miR-150 (10 μM) or antimiR-150 (10 μM). PBLs were recovered and analyzed by flow cytometry. Cells were first gated for singlet on FSC-H vs. FSC-A and lymphocytes were gated on SSC-A vs. FSC-A. (B) Proliferation was measured in total lymphocytes after 72 h of culture according to Ki67 labeling. (C) Cell death was determined in total lymphocytes after 72 h of culture according to a live-dead staining. (D–F) To evaluate cell proliferation after 72 h in culture, PBLs were labeled with anti-CD4, CD8, CD19, and Ki67 antibodies (n = 5). (G–I) To evaluate cell death after 72 h in culture, PBLs were labeled with anti-CD4, CD8, CD19 antibodies and a live-dead stain (n = 6). (J) qPCR analyses of pro-apoptotic genes P53, AIFM2, and PDCD4 expression in PBLs. Cells from 2 control donors were cultured for 72 h with a scramble miRNA, miR-150 or antimiR-150 (10 μM). Gene expression levels were normalized on GAPDH expression. (A–I) p-values were assessed by the Wilcoxon paired test.