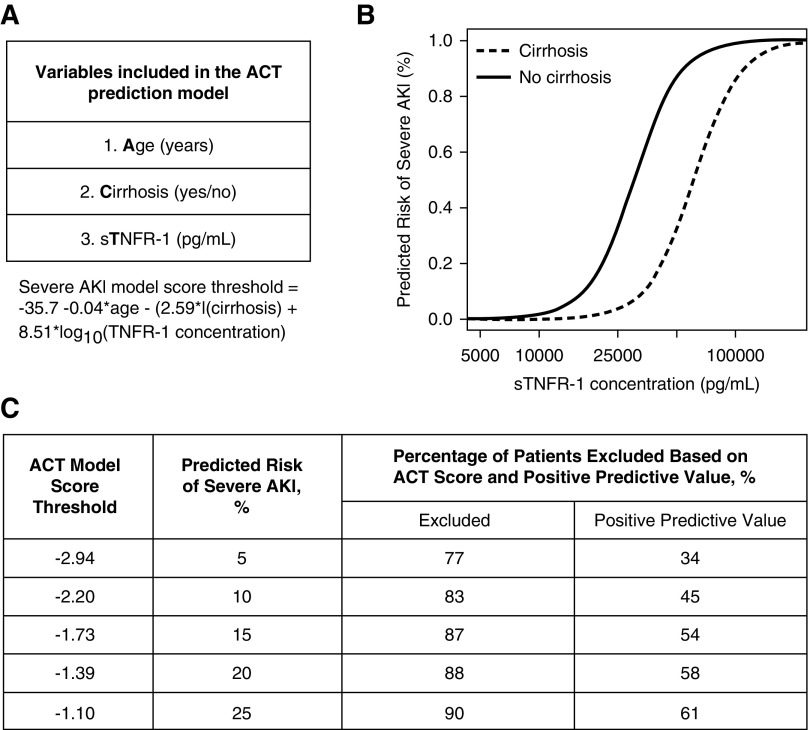
Figure 2.
Performance of three variable prediction model (ACT) varies based on predicted risk of severe AKI. (A) ACT model and the model score threshold equation to determine predicted risk of severe AKI on the basis of age, cirrhosis, and sTNFR-1 concentrations. (B) Predicted risk of severe AKI for a person aged 55 years, with or without cirrhosis and increasing concentrations of sTNFR-1. (C) Performance of the ACT model to predict severe AKI within 72 hours for a range of predicted values. The ACT model score threshold is converted to the probability scale to determine a predicted risk of severe AKI. Excluded is the percentage of patients that had a model score below the respective ACT model score threshold. If this prediction model was used to improve the prognostic enrichment of a clinical trial, then these patients would be “excluded” as they are low risk to develop severe AKI. The positive predictive value is the probability of those with a predicted probability above the model score threshold truly having severe AKI. Data derived from the derivation cohort (n=749).