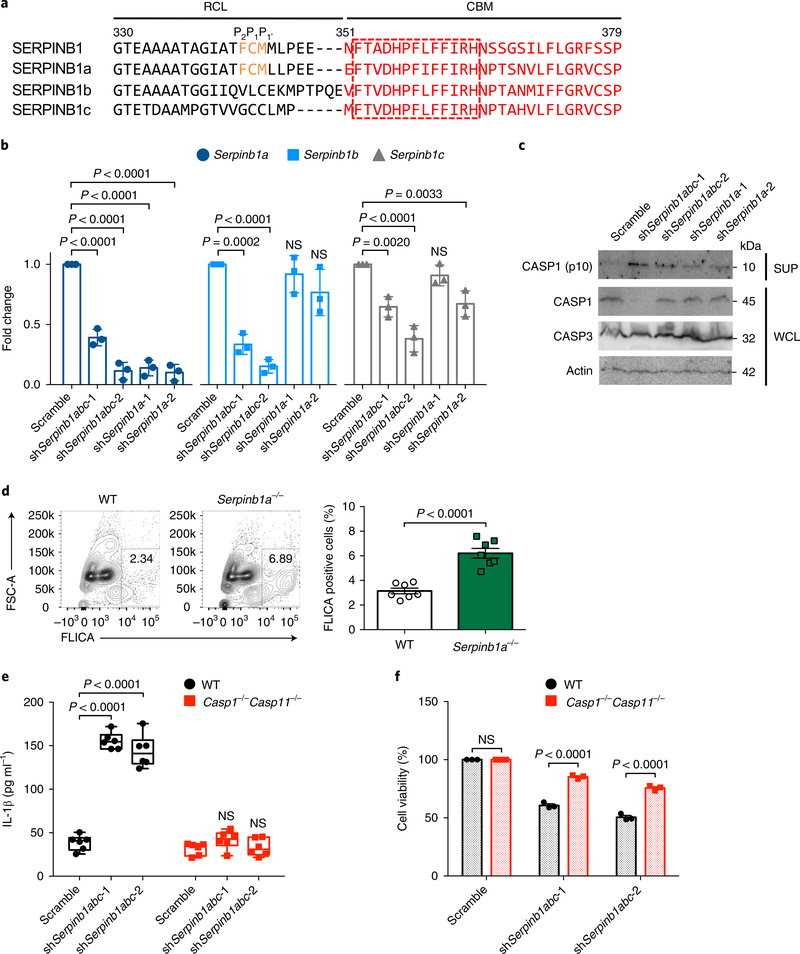
Fig. 4 |. Role of murine SERPINB1 isoforms in caspase-1/–11 inhibition.
a, The RCL and CBM sequence alignment of human SERPINB1 and mouse SERPINB1a, SERPINB1b and SERPINB1c. The conserved P2–P1–P1 residues in the RCL sequence are indicated by orange font, and the CBM sequence is shown in red font. The conserved 13 aa in the CBM sequence are indicated in the red-dotted box. Specified amino acid numbers are based on human SERPINB1. b, Verification of Serpinb1-targeting shRNA’s silencing efficiency by qRT-PCR in DC2.4 cells. mRNA expression was normalized to 18S, and fold change was calculated relative to scramble. c, Immunoblots of cleaved p10 subunit of caspase-1 in DC2.4 cells after Serpinb1a, Serpinb1b and/or Serpinb1c depletion. WCLs and SUPs were obtained at 48 h post-transduction and were immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. d, Caspase-1 activation in Serpinb1a−/− pPMNs. FLICA-positive staining was analyzed by flow cytometry. e,f, IL-1β secretion and cell death after Serpinb1 depletion in BMDMs. Wild-type (WT) and Casp1−/−Casp11−/− BMDMs were transduced with scrambled or pan-Serpinb1 shRNA lentivirus. Cytokines were quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and cell viability was determined by ATP-based assay. Data in c are representative of two independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. from n = 3 independent experiments in b,f and from n = 7 per group, pooled from two independent experiments in d, and as box and whiskers (min to max) from n = 6 pooled from three independent experiments in e. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s comparison relative to scramble in b, by an two-tailed unpaired t-test in d and by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s comparison relative to scramble in e,f.