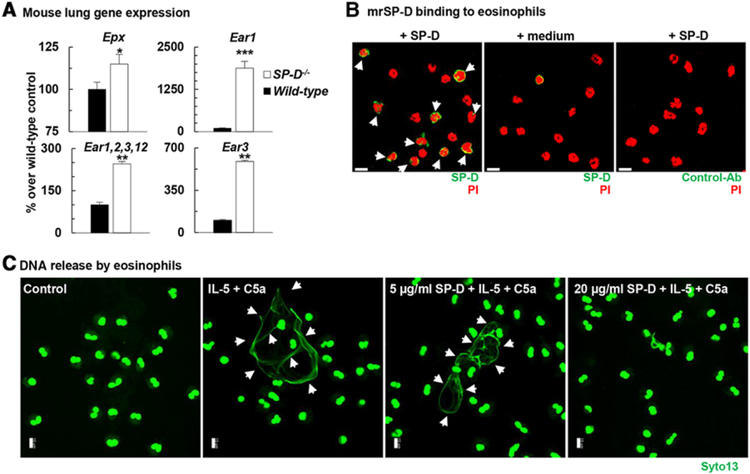
FIGURE 1. SP-D inhibited eosinophil activation and dsDNA (EET) release.
(A): Total RNA was extracted from naïve wild type (C57BL/6, black bars) and SP-D−/− (white bars) lungs. Eosinophil specific gene expression was studied by Affymetrix microarray. Data were standardized to GAPDH and expressed as arbitrary units (% change from the wild-type control mean value). Mean ± SEM of n = 4–6. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (t-test). (B) Immunofluorescent staining of bound SP-D to the surface of mature mouse eosinophils (white arrows) isolated from bone marrow of IL5tg mice. Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) Human recombinant SP-D blocked the formation of EETs by human eosinophils isolated from peripheral blood of healthy donors. (B and C) Confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 10 μm