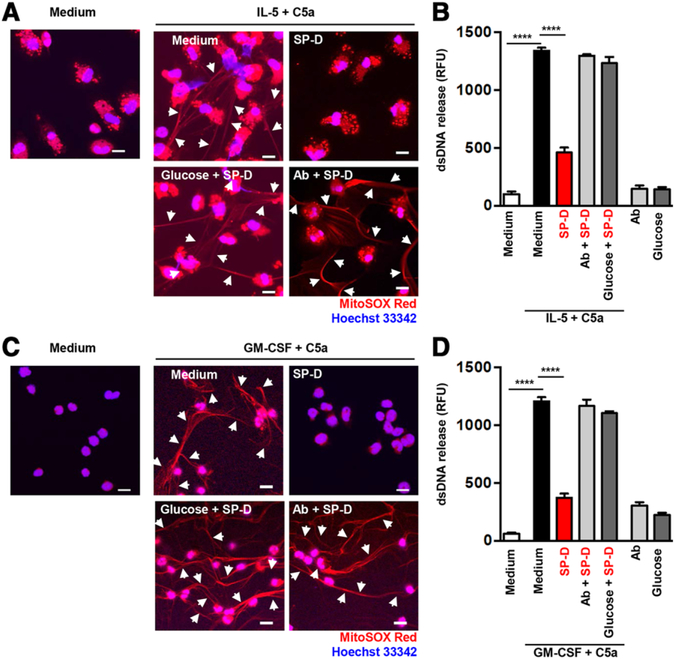
FIGURE 2. SP-D inhibited extracellular DNA release from human and mouse eosinophils in a carbohydrate dependent manner.
Human blood eosinophils (A and B) and mature mouse eosinophils from bone marrow of IL5tg mice (C and D) were analyzed for EET formation. (A and C) EET formation with or without rSP-D (10 μg/mL) alone or together with a neutralizing anti-SP-D Ab (4 μg/mL) or glucose (10 mM), following short-term stimulation as indicated was assessed by confocal microscopy. White arrows indicate extracellular dsDNA. Bars, 10 μm. (B and D) Quantification of released dsDNA in supernatants of activated eosinophils using PicoGreen fluorescent dye. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. ****P < 0.0001