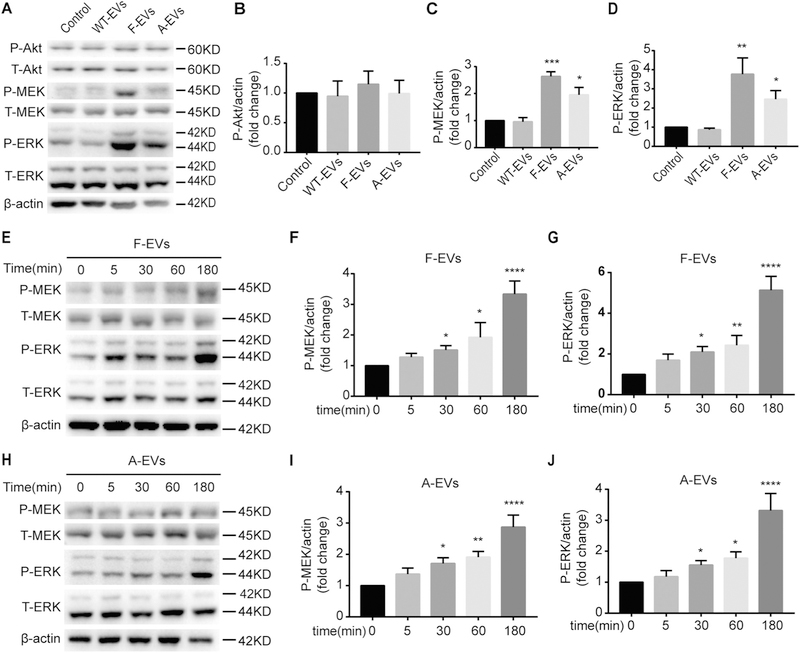
Fig. 5.
iNPC-EVs activate the MEK/ERK pathway of WT-NPCs. (A) The representative western blots showing the expression of P-Akt, P-MEK, and P-ERK after three types of EVs treated WT-NPCs for 1 h in NPC basal medium. (B-D) Densitometric quantifications of the P-Akt (B), P-MEK (C) and P-ERK (D) protein levels were presented as fold change relative to the control. (E-G) Time course of P-MEK and P-ERK phosphorylation were examined after F-EVs treated WT-NPCs for 0, 15, 30, 60, 180 min in NPC basal medium by Western blot. (H-J) Time course of P-MEK and P-ERK phosphorylation were examined after A-EVs treated WT-NPCs for 0, 15, 30, 60, 180 min in NPC basal medium by Western blot. Data were represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *, **, ***, and **** denote p < .05, p < .01, p < .001, and p < .0001 in comparison to control, respectively.