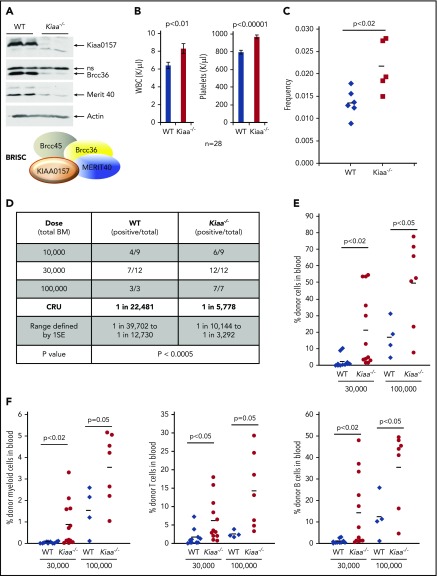
Figure 2.
KIAA0157 deficiency leads to an expansion of phenotypic and functional HSCs. (A) KIAA0157 depletion disrupts the BRISC complex. WB analysis of BM extracts from WT and Kiaa0157−/− (Kiaa−/−) mice. (B) White blood cell (WBC) counts and platelet counts in the peripheral blood of WT and Kiaa−/− mice are shown. N = 28. (C) Frequency of long-term HSCs in WT and Kiaa−/− mice as determined by flow cytometry. Long-term HSC is defined as CD34-Flk2-CD150+LSK. Each symbol represents an individual mouse, and the horizontal lines indicate the mean values. P value was determined by 2-tailed Student t test. (D-F) Functional HSC frequency in WT and Kiaa−/− mice as determined by limiting dilution BM transplantation. Percentage of donor-derived cells in peripheral blood 16 weeks after BM transplantation were analyzed by flow cytometry. Data from 2 to 3 independent experiments were combined. (D) The results are presented as number of positively engrafted mice vs total number of mice analyzed for the indicated doses. Positive engraftment was defined as >1% donor-derived cells in the peripheral blood. Reconstitution frequency and statistical analysis were calculated using ELDA software (http://bioinf.wehi.edu.au/software/elda/). (E-F) Donor chimerism in peripheral blood of the recipient mice transplanted with 3 ×104 and 1 × 105 donor cells along with competitors are shown. (E) Total leukocyte reconstitution. (F) Donor reconstitution in different blood lineages. Each symbol represents an individual mouse; horizontal lines indicate the mean value in each group. P values were calculated by using the 2-tailed Student t test. 1SE, one standard deviation; CRU, competitive repopulating unit; ns, nonspecific.