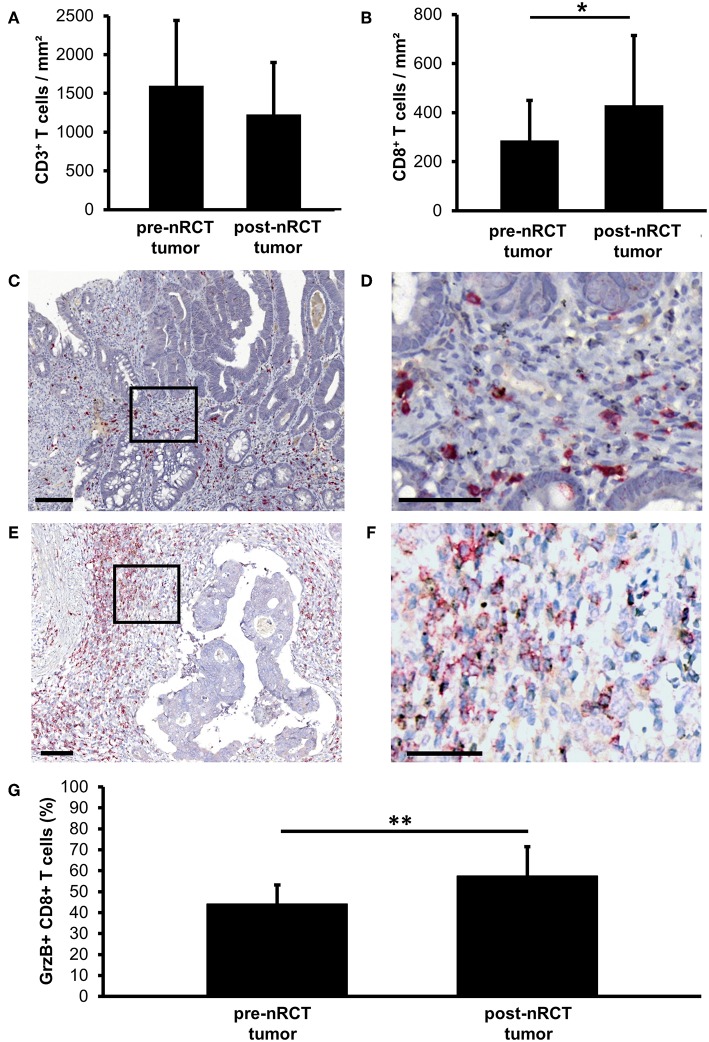
Figure 4.
nRCT significantly increases the proportion of rectal cancer-infiltrating GrzB+ CD8+ T cells. (A–G) Immunohistochemical stainings were performed to explore the frequency of rectal cancer-infiltrating CD3+ T lymphocytes, total CD8+ T lymphocytes, and GrzB+ CD8+ T cells in matched pre-nRCT and post-nRCT tumor samples. The frequency of (A) CD3+ cells and (B) CD8+ T cells in 18 matched pre-nRCT or post-nRCT tumor specimens is presented as mean value ± SD. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference (*p < 0.05). (C–F) As representative examples, the presence of infiltrating GrzB+ CD8+ T cells in an (C,D) untreated and (E,F) nRCT-treated rectal cancer tissue is demonstrated. Scale bars are (C,E) 100 μm or (D,F) 50 μm, respectively. (G) The percentage of GrzB-expressing CD8+ T cells in 18 matched pre-nRCT or post-nRCT tumor specimens is presented as mean value ± SD. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference (**p < 0.01).