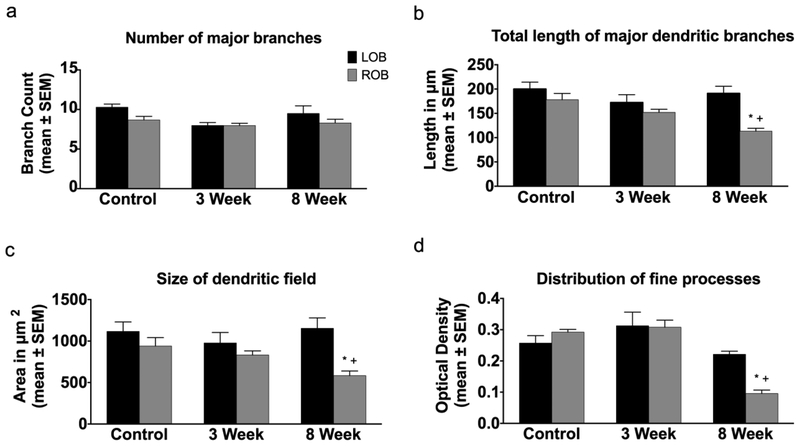
Fig. 3.
Quantitative analysis of the effects of permanent deafferentation on mitral cell dendritic arbors. (a) There were no significant changes in the number of major dendritic branches of mitral cells following 3 and 8 weeks of cautery deafferentation compared to both internal control cells and day 0 unlesioned control fish. (b) While there were no significant changed in the length of dendritic branches 3 weeks post-deafferentation, at 8 weeks post-deafferentation there was a significant reduction in the length of dendritic branches in the deafferented bulb compared to both internal control cells and day 0 unlesioned control cells. (c) At 3 weeks post-deafferentation there was no significant effect on the size of the dendritic field, but with 8 weeks of deafferentation there was a significant decrease in the size of the dendritic field compared to both internal control arbors and day 0 unlesioned control animals. (d) There were no significant changes in the distribution of fine processes with 3 weeks of deafferentation, but with 8 weeks of deafferentation there was a significant decrease in the distribution of fine processes within the dendritic arbor compared to both internal control dendritic arbors and day 0 unlesioned control arbors. * = p<0.05 compared to internal control cells; + = p<0.05 compared to day 0 unlesioned control cells; LOB = left (internal control) olfactory bulb; ROB = right (deafferented) olfactory bulb