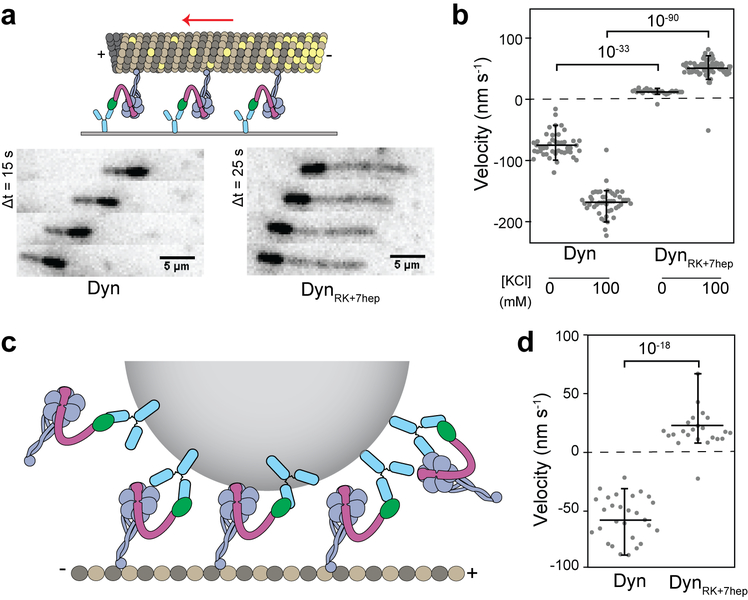
Extended Data Figure 9 ∣. DynRK+7hep monomers exhibit robust plus-end directionality in MT gliding and bead motility assays.
a, (Top) The schematic represents the MT gliding assay with monomeric dynein. (Bottom) Images from time-lapse recordings show gliding of polarity marked MTs by Dyn and DynRK+7hep monomers. While Dyn glides MTs with their plus-end in the lead, DynRK+7hep glides MTs towards the opposite direction. n = 3 biological replicates. b, MT gliding velocity and directionality of Dyn and DynRK+7hep in the presence and absence of 100 mM KCl. Negative velocities correspond to minus-end directionality. n = 45, 47, 27 and 70 from left to right from two independent measurements. c, The schematic of the bead motility assay with monomeric dynein (not to scale). N-terminal GFP-tagged monomers are attached to 860-nm diameter GFP-antibody coated beads from their tail. d, Velocities of the beads driven by Dyn and DynRK+7hep monomers. n = 29 and 24 from left to right from three independent experiments. In b and d, the center line and edges represent mean and 5%-95%, respectively. p-values are calculated from a two-sided t-test.