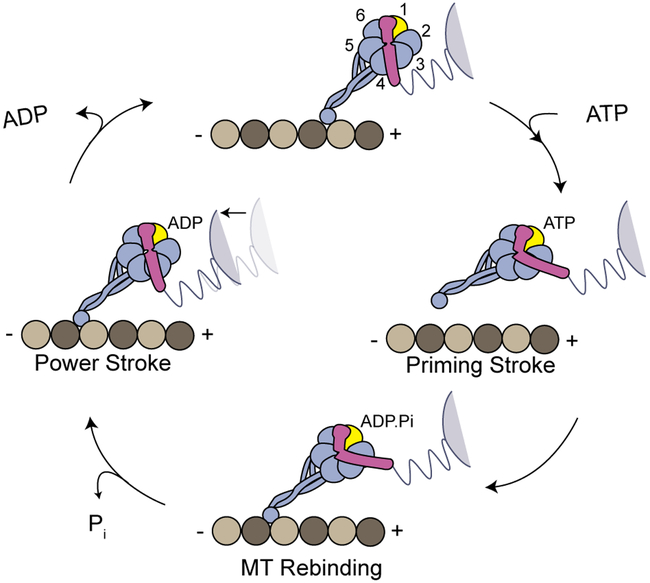
Extended Data Figure 1 ∣. Dynein’s mechanochemical cycle.
a, The AAA+ ring of a dynein monomer lies parallel to the MT and the stalk is tilted towards the plus-end at its base. In the absence of a nucleotide (apo) at AAA1, dynein is tightly bound to MTs and the linker has a straight post-powerstroke conformation, exiting the ring at AAA4. ATP binding to AAA1 (yellow) triggers MT release through a shift in the registry of a coiled-coil stalk and the linker undergoes the priming stroke. At this pre-powerstroke conformation, the linker is bent by a flexible hinge towards the middle of the ring and exits the ring at AAA2. LSV is aligned with the MT long-axis and moves the MTBD towards the minus-end. After ATP hydrolysis, the dynein head re-binds to MT, and releases the inorganic phosphate (Pi). In the ADP bound state, the linker undergoes a force generating powerstroke by moving back to its straight conformation. This pulls the cargo towards the minus end (black arrow). After ADP release, dynein returns back to the apo state for the next cycle.