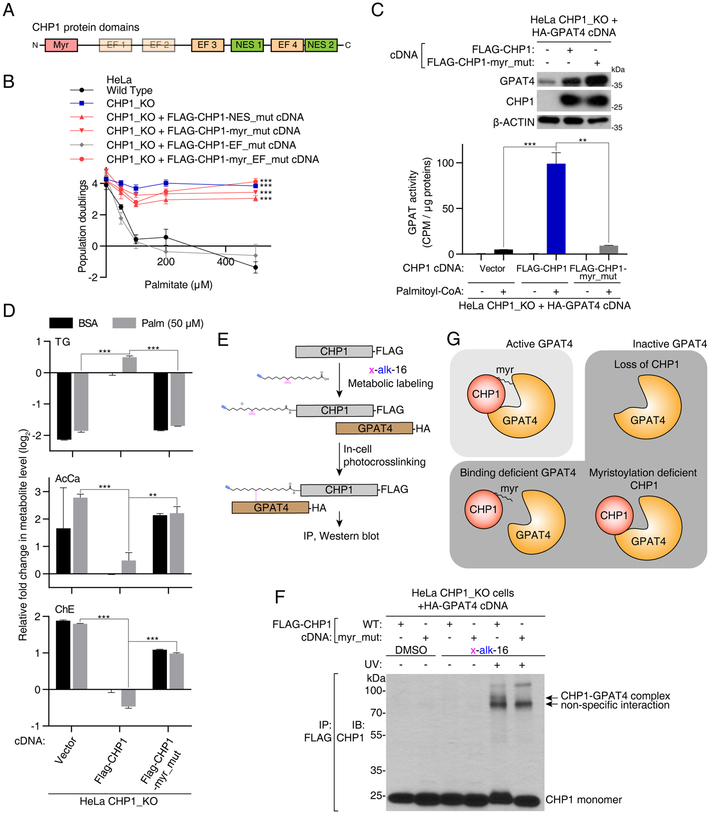
Figure 5. CHP1 activates GPAT4 through its myristoyl moiety.
(A) Schematic of functional protein domains of CHP1.
(B) Identification of functionally relevant residues of CHP1 in glycerolipid metabolism. Fold change in cell number (log2) of HeLa wild type (black), CHP1_KO (blue), CHP1_KO expressing FLAG-CHP1-EF_mut (D123A/D125A/D127A/D164A/D166A/D168A) (gray), FLAG-CHP1-NES_mut (V138A/L139A/V179A/L180A), FLAG-CHP1-myr_mut (G2A/S6A) and FLAG-CHP1-myr_EF_mut (G2A/S6A/D123A/D125A/D127A/D164A/D166A/D168A) (red) cells after a 4-day treatment with the indicated palmitate concentrations (mean ± SD, n=3). ***p < 0.001 versus wild type.
(C) GPAT activity assay of HeLa CHP1_KO cells expressing vector, FLAG-CHP1 and FLAG-CHP1-myr_mut cDNAs. All cell lines are additionally infected with an HA-GPAT4 virus. Immunoblotting analysis of the indicated proteins. β-actin was used as a loading control (top). Cell lysates were incubated with [14C]-glycerol-3-phosphate and with or without palmitoyl-CoA. GPAT activity was quantified as the CPM in the non-polar fraction (mean ± SD, n=3). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus CHP1_KO expressing FLAG-CHP1 (bottom).
(D) Fold change (log2) in indicated lipid groups of HeLa CHP1_KO cells expressing vector, FLAG-CHP1 and FLAG-CHP1-myr_mut cDNAs treated with 50μM palmitate for 24 hrs prior to lipid extraction. Lipid species of the same group were summed. Values were normalized to the average of the untreated CHP1_KO cells expressing FLAG-CHP1 cDNA (mean ± SD, n=3). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus CHP1_KO expressing FLAG-CHP1 cDNA.
(E) Schematic depicting steps to crosslink CHP1 and GPAT4 through a bifunctional fatty acyl group on the myristoylation site of CHP1.
(F) Immunoblot using an antibody against CHP1 on immunoprecipitates with FLAG-CHP1 or FLAG-CHP1-myr_mut in the presence or absence of x-alk-16 photo-crosslinking. Crosslinked complex of CHP1-GPAT4 appeared as a higher band with a combined molecular weight of these two proteins (~80 kDa).
(G) Schematic depicting active and inactive forms of GPAT4. Interaction of CHP1 with GPAT4 alone is necessary but not sufficient for GPAT4 activity. Full GPAT4 activity requires CHP1 to be myristoylated.
See also Figure S6.