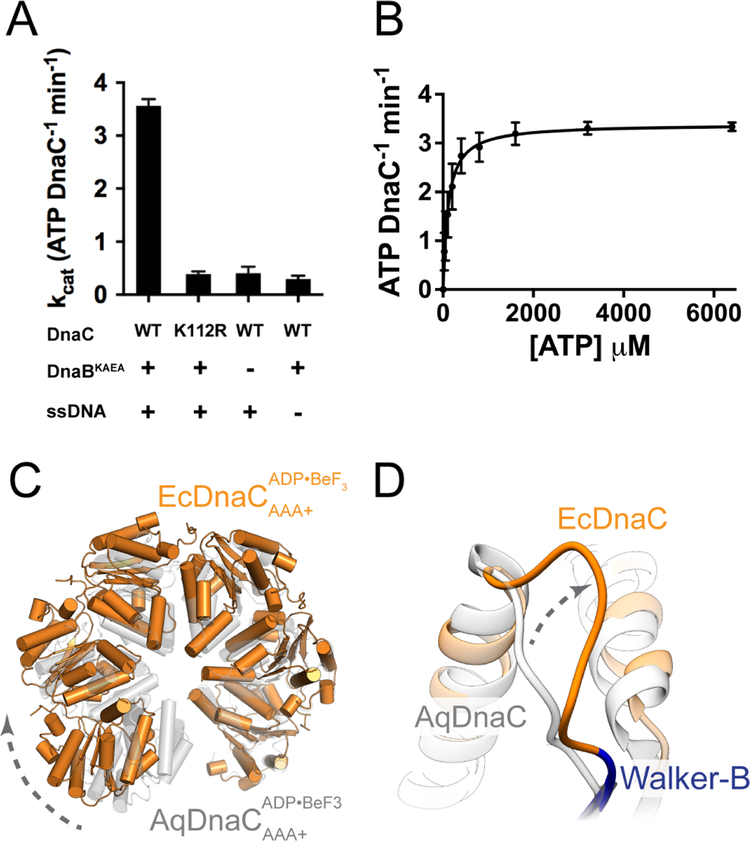
Figure 2. DnaC is a functional AAA+ ATPase. See also Figure S3.
(A) DnaC ATPase activity requires both DnaB and ssDNA. Rates for ATP-hydrolysis were determined for WT and K112R Walker-A mutant using a coupled ATP-hydrolysis assay. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(B) Kinetics of ATP-hydrolysis by DnaC. A coupled ATP-hydrolysis assay was performed using wild type DnaC to calculate hydrolysis rates at various ATP concentrations. Rates were fitted to the Michaelis-Menten equation. Error bars represent the variation over three independent experiments (mean ± SEM).
(C) The helical pitch and curvature of the DnaC hexamer in the complex with the helicase is more expanded than that observed for the isolated DnaC AAA+ domains (PDB 3ECC (Mott et al., 2008)).
(D)The loop adjacent to the Walker-B motif in E. coli DnaC adopts a different configuration from that of A. aeolicus DnaC.