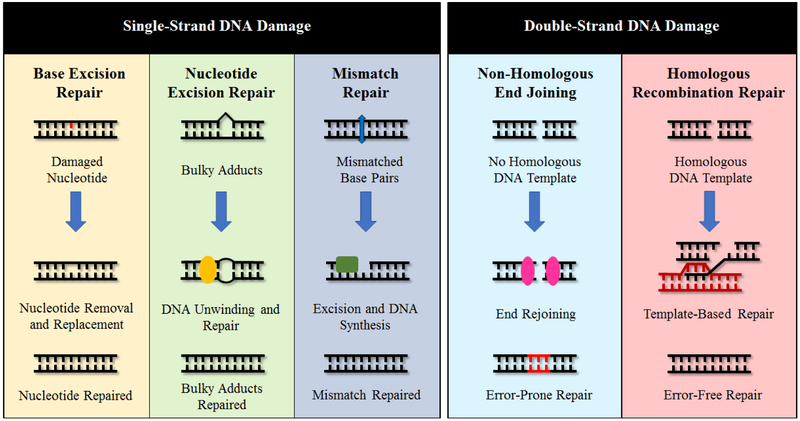
Fig 1.
DNA repair pathways of single-strand DNA (ssDNA) damage and DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). From left to right for ssDNA repair: base excision repair (BER) is used to repair damage to nucleotides that do not significantly alter the DNA structure. Nucleotide excision repair (NER) mends structurally altering DNA damage, such as bulky adducts. Mismatch repair (MMR) fixes pairs of nucleotides that were mismatched during DNA synthesis. Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repairs DNA DSBs without the use of a homologous DNA template by rejoining the broken DNA ends together and is prone to introducing errors. Homologous recombination repair (HRR) uses a homologous DNA template to repair DNA DSBs without error.