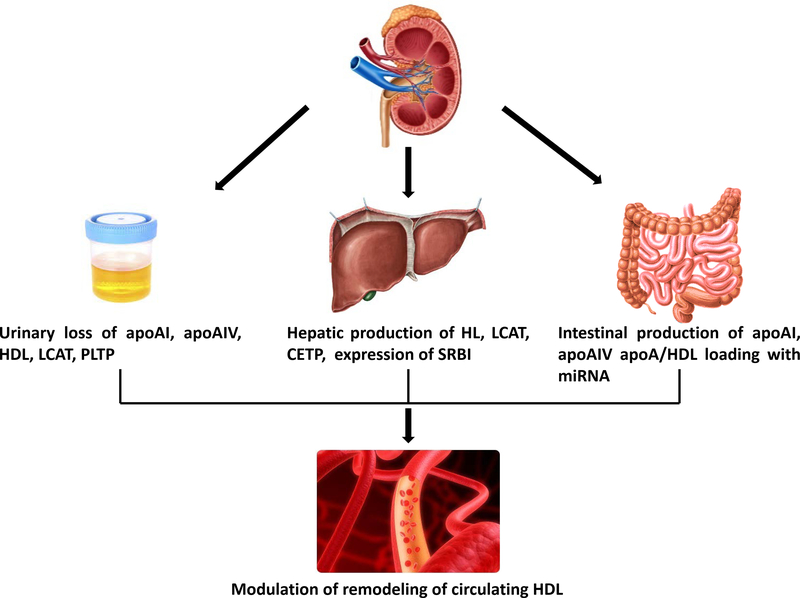
Figure 2. Kidney regulation of HDL metabolism.
Kidneys can filter, reabsorb and lose HDL and its components. All these processes are activated when injury involves disruption of the glomerular filtration barrier; renal injury activates hepatic production and metabolism of HDL and its components; renal injury activates intestinal production of apoAI and loads cargo onto HDL modifying the particles.
apoAI, apolipoprotein AI; apoAIV, apolipoprotein IV; HDL, high density lipoprotein; LCAT, lecithin cholesteryl ester acyltransferase; PLTP, phospholipid transfer protein; HL, hepatic lipase; CETP, cholesterol ester transfer protein; SRBI, scavenger receptor BI.