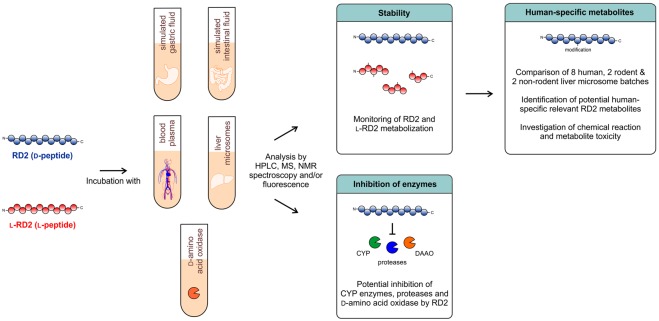
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the methodological approaches. It was investigated whether the D-peptide RD2 is a substrate or inhibitor for enzymes contained in simulated gastric and intestinal fluid, human blood plasma and human liver microsomes or for the D-amino acid oxidase. RD2’s mirror image l-RD2 served as comparative substance. Potential human-specific metabolites generated in liver microsomes were identified and characterized.