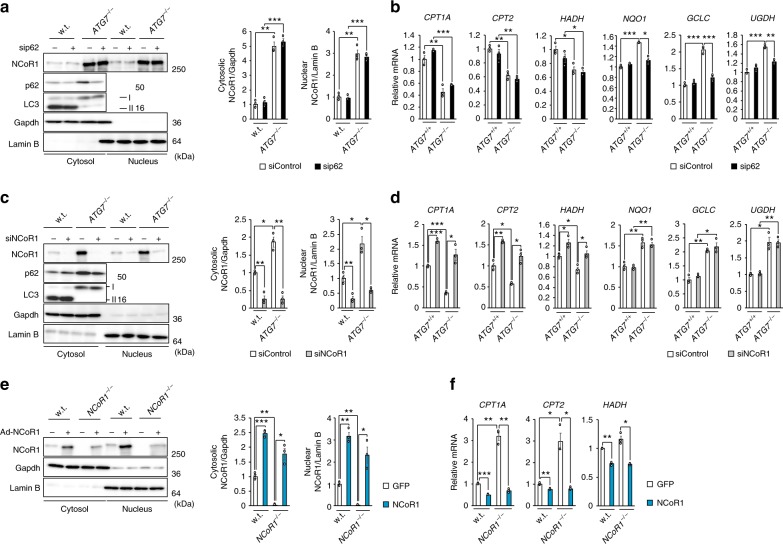
Fig. 4.
NCoR1-dependent PPARα-inactivation in autophagy-incompetent cells. a, c Immunoblot analysis. Parental and ATG7-knockout HepG2 cells (#14) were treated with siRNA for p62 (a) and NCoR1 (c). Thereafter, both nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were prepared and subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Data are representative of three separate experiments. Bar graphs indicate the quantitative densitometric analyses of cytoplasmic and nuclear NCoR1 relative to Gapdh and Lamin B, respectively. b, d Real-time PCR analysis. Total RNAs were prepared from cells described in b and d. Values were normalized against the amount of mRNA in parental HepG2 cells treated with control siRNA. The experiments were performed three times. e Immunoblot analysis. GFP or NCoR1 was exogenously expressed in wild-type and NCoR1-knockout HepG2 cells using the adenovirus system. Forty-eight hours after infection, both nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were prepared from cells and subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Data shown are representative of three separate experiments. Bar graphs indicate the quantitative densitometric analyses of cytoplasmic and nuclear NCoR1 relative to Gapdh and Lamin B, respectively. f Real-time PCR analysis. Total RNAs were prepared from cells described in e. Values were normalized against the amount of mRNA in GFP-expressing wild-type HepG2 cells. The experiments were performed three times. Data are means ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 as determined by Welch’s t-test