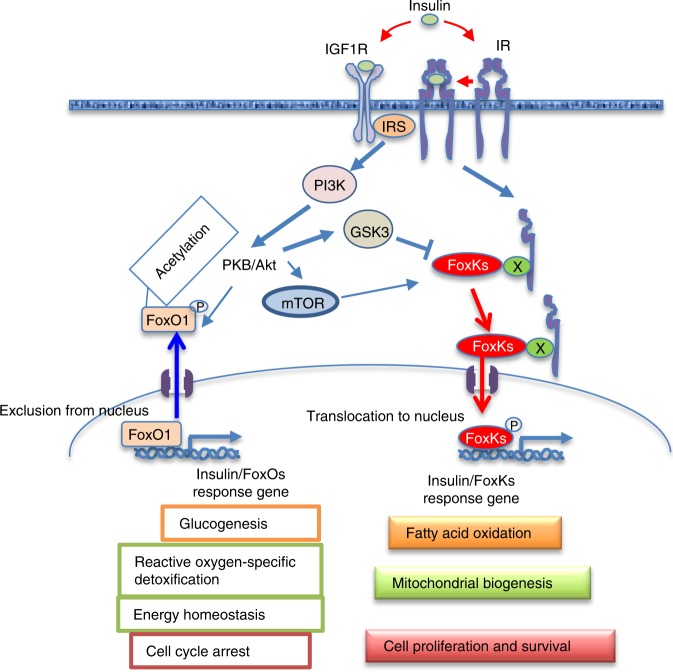
Fig. 8.
Schematic model of insulin regulation of FoxK1/K2 and FoxOs in cellular function. The FoxK Forkhead transcription factors translocate from the cytoplasm to nucleus reciprocally to the translocation of FoxO1. FoxK translocation to the nucleus is dependent on the Akt-mTOR pathway, while its localization to the cytoplasm in the basal state is dependent on GSK3. Once in the nucleus, FoxKs play important roles in regulation of genes, fatty acid oxidation, mitochondrial biogenesis, cell proliferation and survival. Where other unknown proteins (named here X) are in the FoxK and IR/IGF1R protein-protein complexes remains to be determined