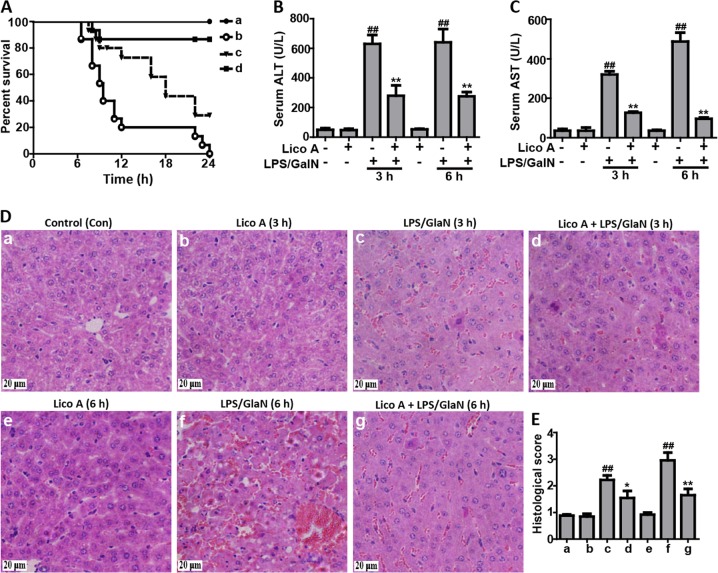
Fig. 1. The protective effects of Lico A-treated on LPS/GalN-induced ALI.
Lico A (50 or 100 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to mice for twice (interval for 12 h), followed by exposed to LPS (30 μg/kg) and D-GalN (600 mg/kg), which is abbreviated as LPS/GalN. a Survival rate of mice was observed within 24 h after LPS/GalN administration. (a) Control and Lico A (100 mg/kg) group; (b) LPS/GalN group; (c) Lico A (50 mg/kg)+LPS/GalN; (d) Lico A (100 mg/kg)+LPS/GalN. b, c Injection with LPS/GalN for 3 h and 6 h, serum of mice were collected for assessment of ALT and AST levels. d Livers (n = 5) from each experimental group were subjected to stain with hematoxylin and eosin (h and e)-stained (magnification ×400). e The stained sections were defined as using a four-point scale from 1 to 4, with 1, 2, 3, and 4, which represents (1) no damage, (2) mild damage, (3) moderate damage, and (4) severe damage, respectively. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. All data are presented as means±SEM (n = 5 in each group). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. Control group; ##p < 0.01 vs LPS/GalN group