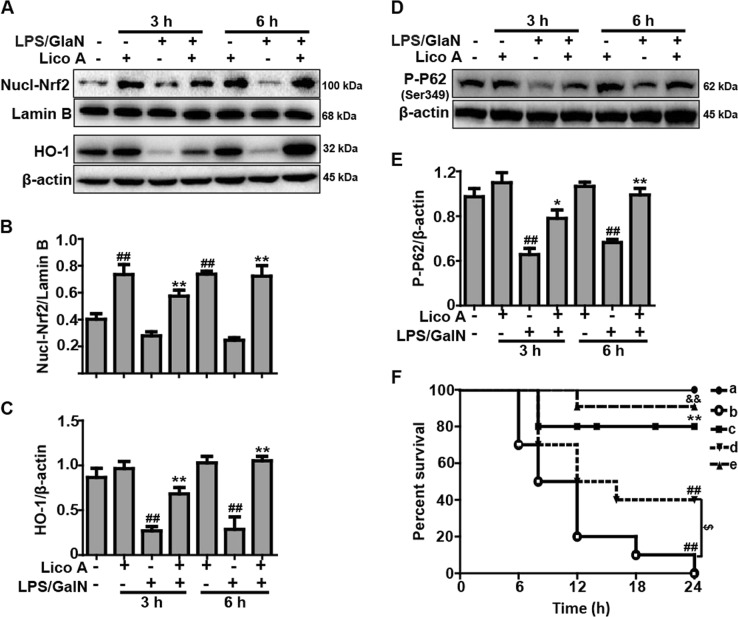
Fig. 6. Effects of Lico A-treated on the upregulation of P62-Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in LPS/GalN-induced ALI.
a Liver tissues were collected from the mice 3 h and 6 h after LPS/GalN challenge and analyzed by western blot for the assessment of the nuclear levels of Nrf2, and HO-1 protein expression. Moreover, d the effect of Lico A on the phosphorylation of P62 at ser349. b, c, e Quantification of relative protein expression was performed by densitometric analysis. Lamin B and β-actin were used as an internal control. WT and Nrf2−/− mice were intraperitoneally injected Lico A (100 mg/kg) with mice for twice at a 12-h (interval for 12 h), followed by subjected to LPS/GalN. f The survival rates of the mice (n = 10/group) were observed within 24 h after LPS (30 μg/kg) and GalN (600 mg/kg) exposure. (a) WT/KO Control and Lico A group; (b) WT LPS/GalN group; (c) WT Lico A+LPS/GalN group; (d) KO LPS/GalN group; (e) KO Lico A+LPS/GalN group. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. All data are presented as means±SEM (n = 5/group). ##p < 0.01 vs. WT control group; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. WT LPS/GalN group; $$p < 0.01 vs. KO control group; &p < 0.01 vs. KO LPS/GalN group