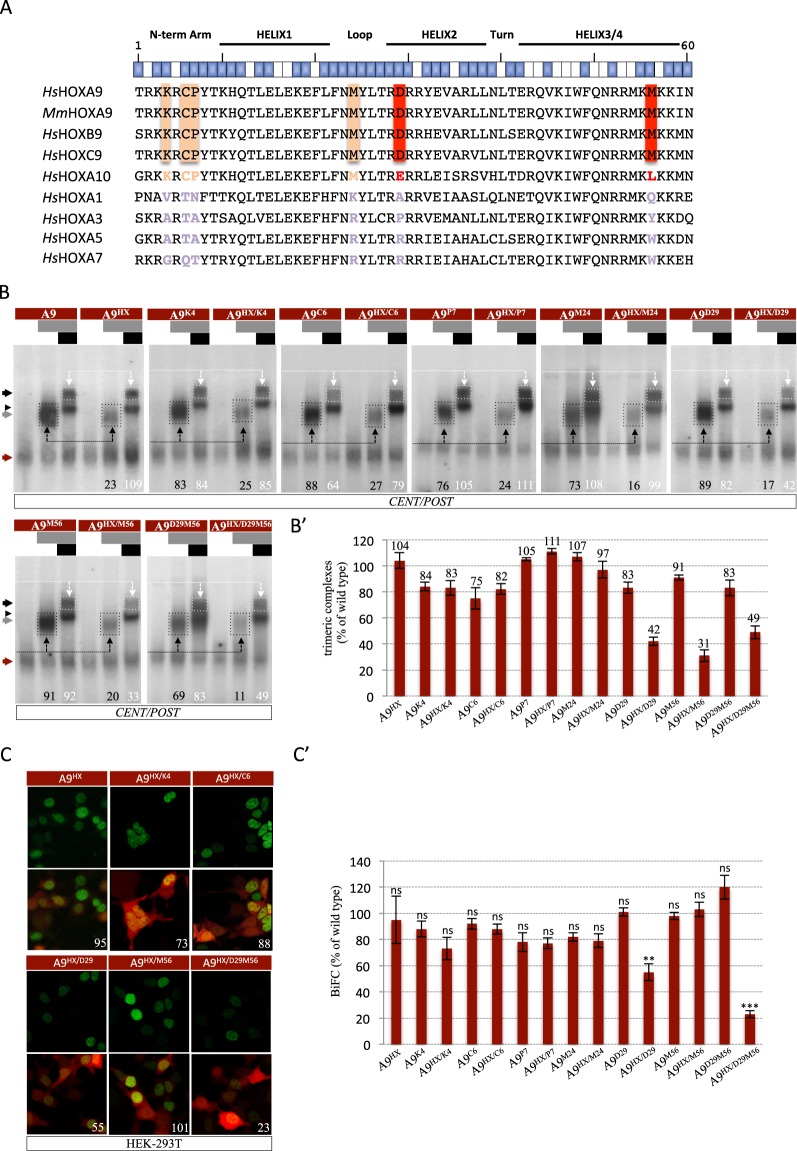
Figure 3.
Paralog-specific residues of the HOXA9 HD are important for the interaction with TALE cofactors. (A) Sequence alignment of the HD of HOXA9 and other human (Homo sapiens, Hs) or mouse (Mus musculus, Mm) HOX proteins. The global structure and orientation of the aliphatic chain of each residue is indicated above the sequences. Blue and white boxes symbolize residues that are accessible or not for protein-protein interactions, respectively (based on30). Residues that are conserved in paralog groups 9 and 10 or only in paralog group 9 are highlighted in light orange or red, respectively. (B) Band shift experiments between HOXA9 constructs and PBX1, or PBX1 and MEIS1 on the CENT/POST nucleotide probe, as indicated. Color code and quantifications of HOXA9/TALE protein complexes are as in Fig. 2. (B’) Quantification of trimeric complexes with the different mutated forms of HOXA9 from three independent experiments. (C) Illustrative confocal pictures of BiFC between different HOXA9 constructs and PBX1 in HEK cells, as indicated. Color code is as in Fig. 2. (C’) Quantification of BiFC between the different mutated forms of HOXA9 and PBX1 from three independent experiments. Significance is shown relative to BiFC with wild type HOXA9 and was evaluated using t test (***p < 0,001; **p < 0,01; ns, nonsignificant).