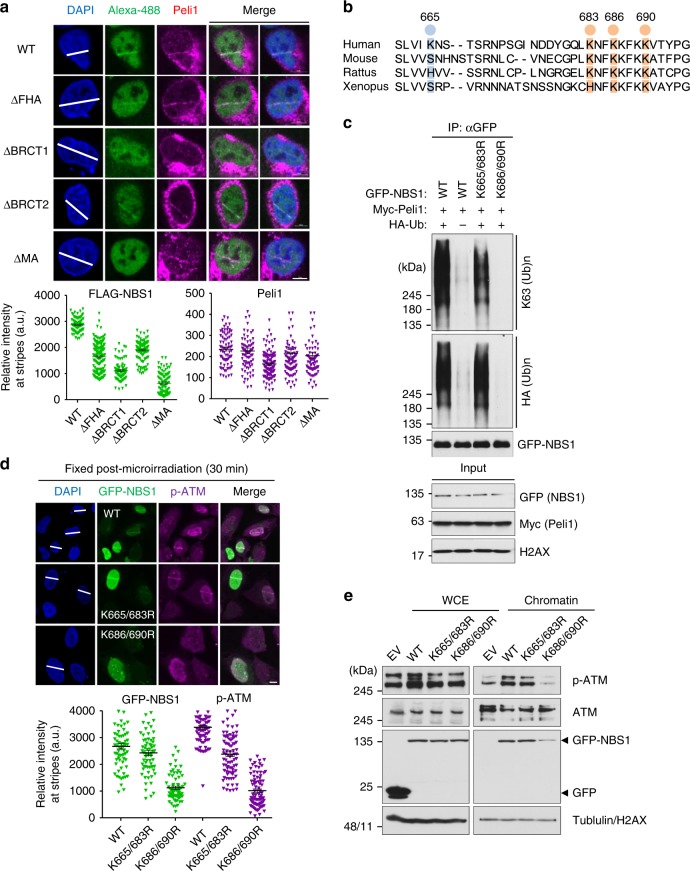
Fig. 7.
Peli1 ubiquitinates NBS1 at lysine 686 and 690 that regulate NBS1 and active ATM retention at damaged sites. a FLAG-NBS1 WT and truncated mutants were transfected into U2OS cells. At 48 h post transfections, cells were microirradated and fixed at 30 min post micro-irradiation. Recruitments of Peli1 and FLAG-NBS1 constructs were evaluated with anti-FLAG and anti-Peli1 antibodies (upper panels). Quantitative analysis of FLAG-NBS1 constructs and Peli1 at laser stripes was also performed. The intensity of each constructs at laser stripes was determined by averaging values from 20 cells and graphed (lower panels). Scale bars, 10 μm. b Comparison of conserved lysine residues of C-terminal NBS1 in eukaryotes. c 293T cells were transfected with GFP-NBS1 WT and lysine-dead (K665/683R and K686/690R) mutants in combination with Myc-Peli1 WT and HA-Ub. Immunoprecipitated NBS1 with anti-GFP antibody was detected with anti-HA and anti-K63 antibodies. d Cells transfected with GFP-Peli1 WT, K665/683R, and K686/690R mutants were subjected to micro-irradiation at 24 h post transfection with endogenous NBS1 3′-UTR-targeting siRNA. At 30 min post micro-irradiation, micro-irradiated cells were fixed and immunostained with anti-p-ATM antibody (upper panels). Quantitative analysis of GFP-NBS1 constructs and p-ATM at laser stripes was also performed. The intensity at laser stripes was determined by averaging values from 20 cells and graphed (lower panels). Scale bars, 10 μm. e 293T cells were transfected with GFP-NBS1 WT, K665/683R, or K686/690R mutants. At 48 h post transfection, DSB-mimetic drug phleomycin (50 μg/ml) was used to treat cells. After washing out, whole cell extracts and chromatin fraction were collected 30 min later. Indicated antibodies were used to detect signals