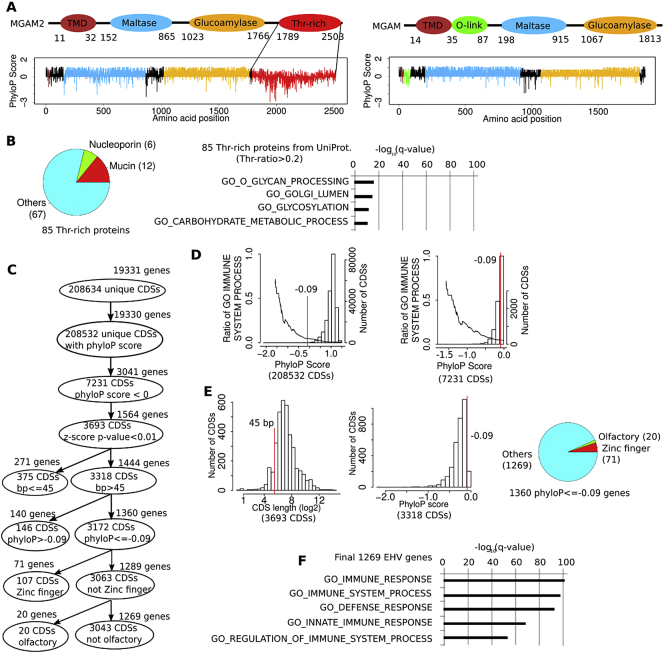
Fig. 3.
Evolutionarily hypervariable (EHV) genes, including MGAM2, are associated with immune response.
A: MGAM2 contains an extra threonine-rich and EHV domain at the C-terminus, compared to MGAM. PhyloP scores are 20 mammals-based, with positive values indicating conservation and negative values indicating variation.
B: A total of 85 proteins with threonine-rich domains, identified from UniProt, are not enriched in immune-related functions.
C: We established a pipeline to identify genes with at least one EHV CDS via multi-step selections, including z-score tests and cutoffs on CDS length and phyloP score (see Methods).
D: The proportion of immune-related genes increases as the phyloP scores of their CDSs decrease. The bars (the right Y-axis) indicate the distribution the average phyloP scores of all CDSs (left image) or CDSs with negative phyloP scores (right image) in the human genome. The line (the left Y-axis) represents the distribution of the proportion of immune-related genes. Red line indicates the average phyloP score of the last CDS of MGAM2.
E: Left two plots indicate the distribution of the CDS length and phyloP score after z-score test selection shown in C, with red lines specifying cutoffs used for further selection. The pie chart indicates the composition of the selected 1360 genes with EHV CDSs.
F: The final EHV genes are significantly enriched in immune response-related functions.
See also Table S3 and Fig. S3 (based on conservation of 100 species). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)