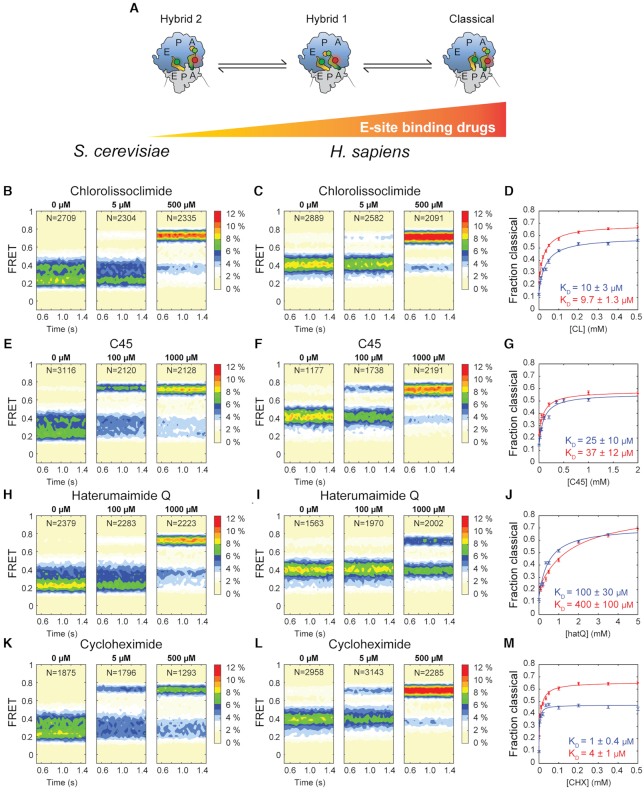
Figure 4.
smFRET measurements of drug titrations on the yeast and human pre-translocation ribosome. Ribosomes containing P-site bound Cy3-tRNAfMet and A-site bound Met-Phe-Cy5-tRNAPhe were imaged at different drug concentrations and FRET between the two bound tRNA molecules was recorded. The ribosomes occupied three distinct FRET states that correspond to the Hybrid 2, Hybrid 1 and Classical tRNA conformations. (A) Schematic representation of the experiment: as the concentration of E-site binding drugs increases the ribosome increasingly favors classical over hybrid tRNA states. (B/C) Population FRET histograms of yeast and human pre-translocation ribosomes at the indicated concentrations of CL. N indicates the number of individual FRET traces used to construct the histograms. (D) The fraction of ribosomes in the high-FRET classical tRNA conformation as a function of CL concentration, estimated from data as in B and C, where blue data points indicate yeast and red data points indicate human. The solid lines represent fits of Eq. 1 to the data (Materials and methods), the blue KD quantifies the affinity for the yeast ribosome and the red that for the human ribosome. (E, F) Population FRET histograms of yeast and human pre-translocation ribosomes at the indicated concentrations of C45. (G) The fraction of ribosomes in the high-FRET classical tRNA conformation as a function of CL concentration, estimated from data as in E and F. (H, I) Population FRET histograms of yeast and human pre-translocation ribosomes at the indicated concentrations of hatQ. (J) The fraction of ribosomes in the high-FRET classical tRNA conformation as a function of hatQ concentration, estimated from data as in H and I. (K, L) Population FRET histograms of yeast and human pre-translocation ribosomes at the indicated concentrations of CHX. (M) The fraction of ribosomes in the high-FRET classical tRNA conformation as a function of CHX concentration, estimated from data as in K and L. All error bars represent SEM.