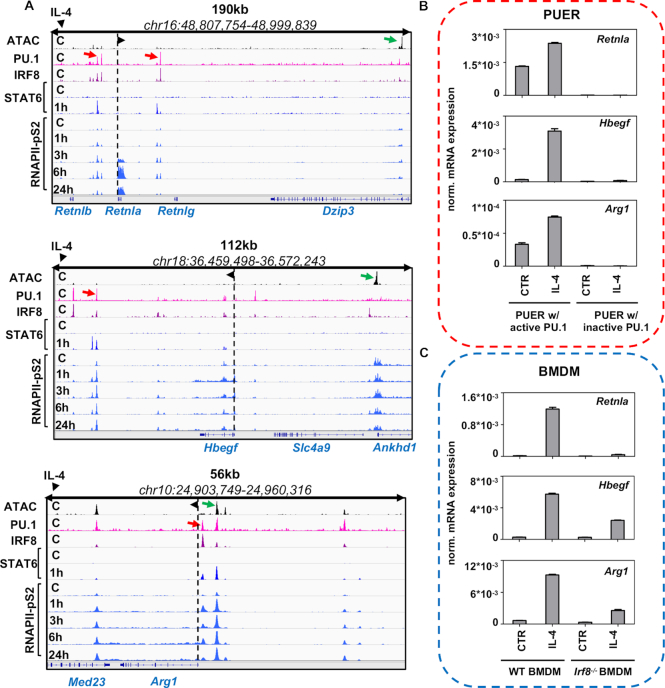
Figure 4.
PU.1+IRF8 co-labelled regulatory elements are important for the cellular response to IL-4. (A) IGV snapshots of three alternative macrophage polarization specific marker gene loci (Retnla, Hbegf and Arg1) with PU.1+IRF8 co-labelled regulatory elements (PU.1+IRF8 co-LREs) that bind STAT6 upon IL-4 treatment and recruit the elongation-specific form of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII-pS2). Green arrows represent highly accessible chromatin regions, while red arrows depict PU.1+IRF8 co-LREs. Dashed lines with arrowheads represent the transcription start site and the direction of the gene. (B) Gene expression measurements by RT-qPCR at the mRNA level on the three alternative polarization marker genes (Rentla, Hbegf and Arg1) from PUER cells. PUER cells were exposed to tamoxifen for 24 h (PUER w/ active PU.1) or left untreated (PUER w/ inactive PU.1) followed by 3 h of IL-4 stimulation. The expression of mRNAs are normalized to the expression of the housekeeping gene Ppia. (C) Gene expression measurements of alternative polarization marker genes (Rentla, Hbegf and Arg1) by RT-qPCR at the mRNA level from wild-type bone marrow-derived macrophages (WT BMDM) or Irf8-deficient BMDMs (Irf8−/− BMDM) after exposed to IL-4 for 3 h. Expression values are normalized to Ppia.