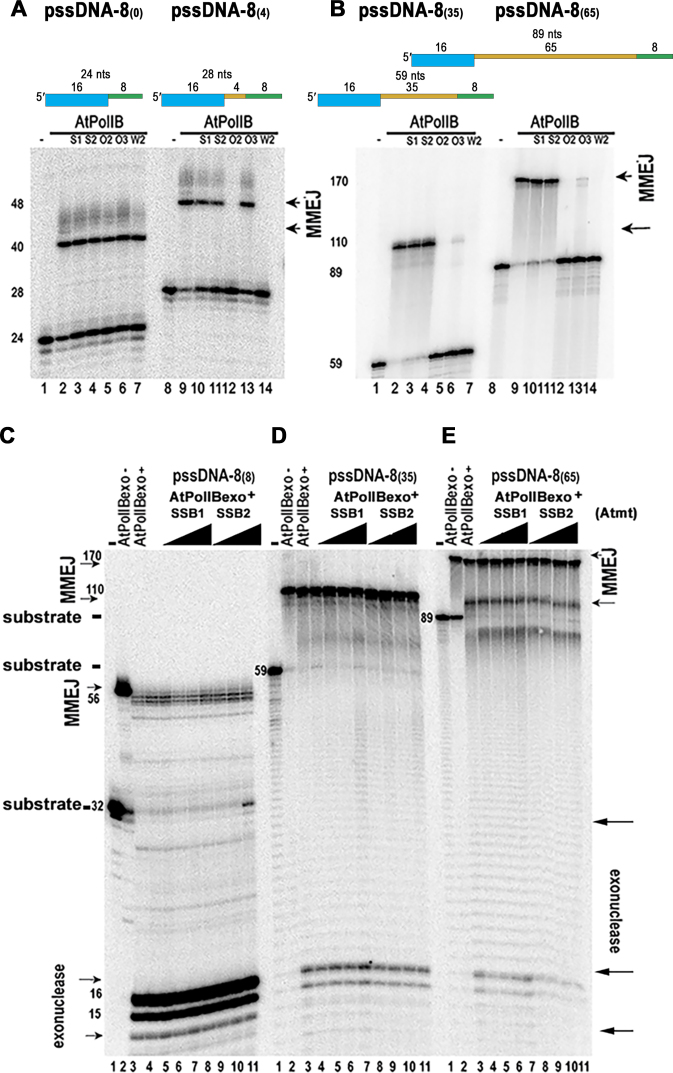
Figure 8.
AtSSBs and single-stranded length of the DNA break regulate MMEJ. (A, B) Unique SSB from plant organelles hamper MMEJ on substrates with single-stranded regions longer than 8 nts. MMEJ formation by AtPolIs in the presence of plant SSBs (AtmtSSB1, S1; AtmtSSB2, S2; AtOSB2, O2; AtOSB3, O3; and AtWhirly2, W2) in MMEJ substrates with a constant microhomologous sequence of 8 nts, but varying single-stranded regions of 8 (panel A, lanes 1 to 7),12 (panel A, lanes 8–14) 43 (panel B, lanes 1–7) and 73 nts (panel B, lanes 8–14). The length of the MMEJ, single-stranded region and total oligonucleotide length of the substrates are indicated in the upper part of the panel. The length of the substrates and MMEJ products are indicated by arrows. (C–E) Wild-type AtPolIA and AtPolIB execute MMEJ with minimal exonucleolysis on substrates with single-stranded regions longer than 16 nts. (C) MMEJ reaction by AtPolIA (lanes 3–6) and AtPolIB (lanes 7–11) on a pssDNA with 8 bases of microhomologous sequence and 8 extra-bases of single-stranded DNA. The labeled substrate is indicated in lane 1 and the MMEJ product by and exonuclease deficient AtPolIB is shown in lane 2. (D and E) As in C, but with a substrate containing 35 nts or 65 nts of extra single-stranded DNA respectively.