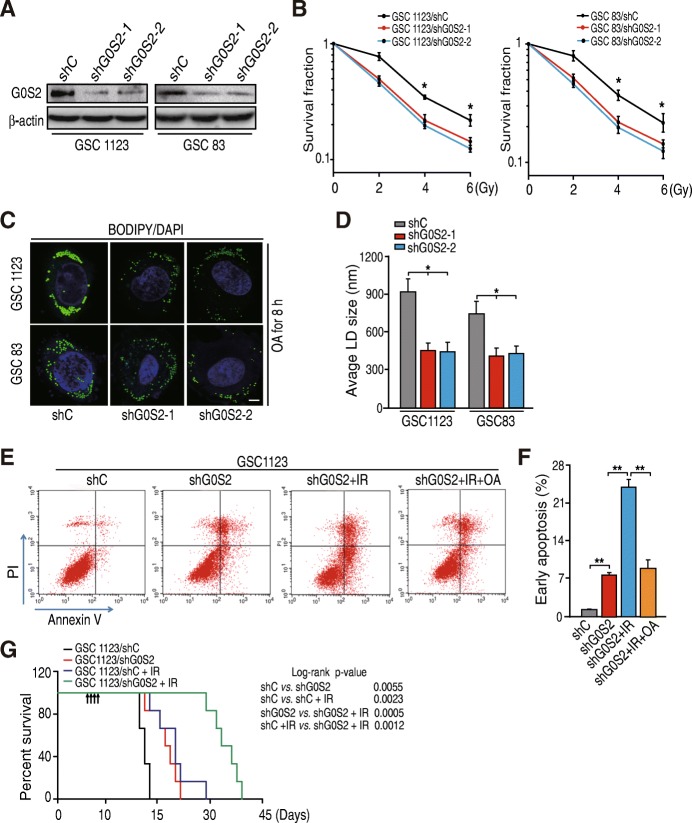
Fig. 2.
Knockdown of G0S2 enhances glioma radiation response. a WB analysis of knockdown of G0S2 with two different shRNAs (shG0S2–1 and shG0S2–2) in GSC 1123 and GSC 83 cell lines. b Clonogenic survival assay of GSC 1123 and GSC 83 cell lines transduced with control shRNA (shC) or G0S2 shRNAs (shG0S2–1 and shG0S2–2). Colonies formed by surviving cells 15 days after IR are shown. c Immunofluorescence staining with BODIPY 493/503 fluorescence dye was performed to lipid droplets (LD). Two sets of GSCs were incubated under normal growth conditions with 100 μM of oleic acid (OA) complexed to albumin at a molar ratio of 8:1 for 16 h. Bars, 5 μm. d Quantification of lipid droplet diameter. An average diameter of 30 lipid droplets per cell over 30 cells for each point was measured. e OA treatment inhibited G0S2 shRNA-enhanced cell apoptosis induced by IR. GSC 1123 cells transduced with a shRNA were incubated with 400 μM of OA or vehicle treated with or without 10-Gy IR, and then cell apoptosis were analyzed by FACS. f Quantification of early cell apoptosis. g Survival curves for mice implantation with 4 × 103 cells of GSC 1123/shC or GSC 1123/shG0S2 and left untreated or given daily dosed 2.5 Gy IR from day 7 to 10 after cell implantation. Arrows, radiation treatment times. Data represent two independent experiments with 6 mice per group with similar results. Error bars, SD. *, p < 0.05. **, p < 0.01