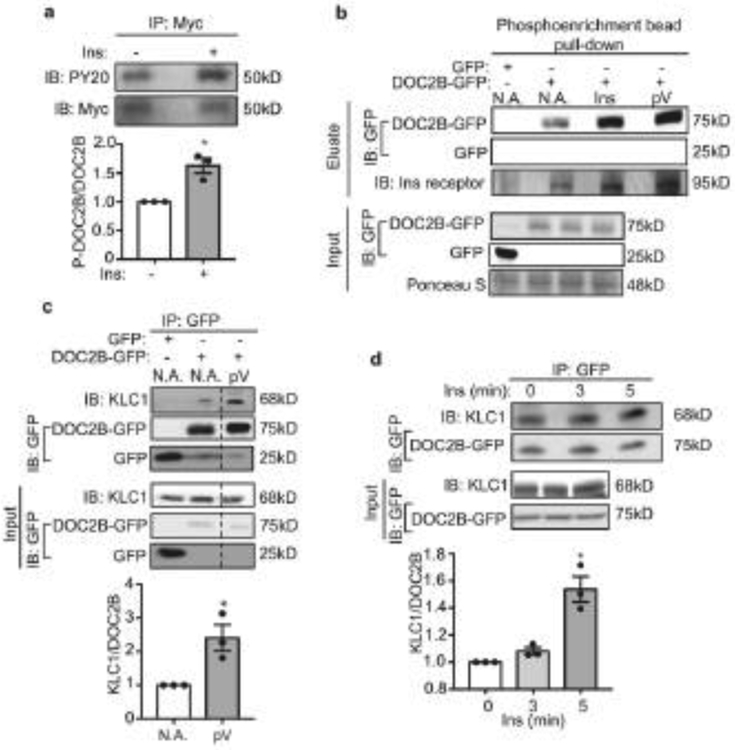
Fig. 6.
Insulin stimulation phosphorylates DOC2B and enhances its interaction with KLC1. (a) DOC2B phosphorylation measured as anti-PY20 immunoreactivity after anti-Myc immunoprecipitation of DOC2B-Myc from the hindlimbs of mice injected i.p. with saline or insulin. Total DOC2B-Myc level was used as a control. (b) DOC2B phosphorylation in L6-GLUT4-myc myoblasts after insulin or pervanadate treatment using a phosphorylated protein enrichment column followed by immunoblotting. GFP and DOC2B-GFP were detected using anti-GFP at 25 kDa and 75 kDa, respectively. INSR was used as a control for the action of insulin and pV. (c) Effect of pervanadate treatment on the DOC2B–KLC1 interaction, measured using immunoprecipitation with GFP antibody-conjugated Sepharose beads and immunoblotting with antibodies to KLC1 at 68 kDa or GFP for DOC2B-GFP and GFP at 75 kDa and 25 kDa, respectively (n=3). (d) Detection of the DOC2B–KLC1 interaction in L6-GLUT4-myc myoblasts after insulin stimulation for 0, 3 and 5 min using the immunoprecipitation strategy described in (c) (n=3). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05 vs control (without insulin in a, d; without pervanadate [NA] in c). Dashed vertical lines indicate splicing of lanes within the same gel exposure. IB, immunoblot; Ins, insulin; IP: immunoprecipitation; NA, no addition; pV, pervanadate