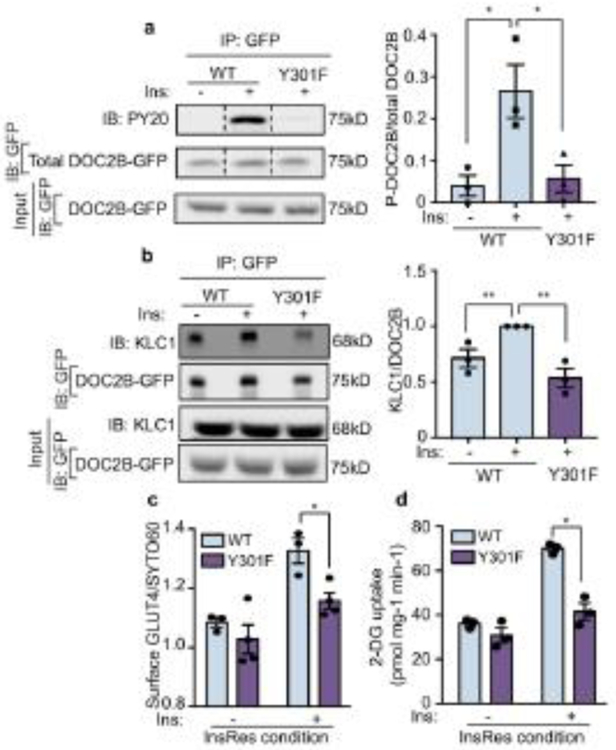
Fig. 8.
Y301F mutation in the C2B domain of DOC2B attenuates the DOC2B–KLC1 interaction and blocks the protective effects of DOC2B. (a) Phosphorylated DOC2B-GFP measured using anti-GFP immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting with anti-PY20. Total DOC2B-GFP in the immunoprecipitated and the input fraction are shown as controls. (b) Detection of KLC1–DOC2B association using anti-GFP immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting with antibodies to KLC1, and to GFP for detection of DOC2B-GFP-WT and DOC2B-GFP-Y301F proteins at 75 kDa (n=3). (c) PM GLUT4 level in myoblasts transfected to express WT DOC2B or the Y301F mutant. GLUT4 levels were measured under basal conditions (−) and after 100 nmol/l insulin stimulation for 20 min. The immunofluorescence intensity of cell-surface GLUT4 was normalised to the nucleic acid staining dye SYTO 60. (d) 2-DG uptake in myotubes transduced to express WT DOC2B or the Y301F mutant. The myotubes were incubated under InsRes conditions and 2-DG uptake was measured in response to insulin stimulation (100 nmol/l) (n=3); *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 as shown. Dashed vertical lines indicate splicing of lanes within the same gel exposure. IB, immunoblot; Ins, insulin; IP, immunoprecipitation