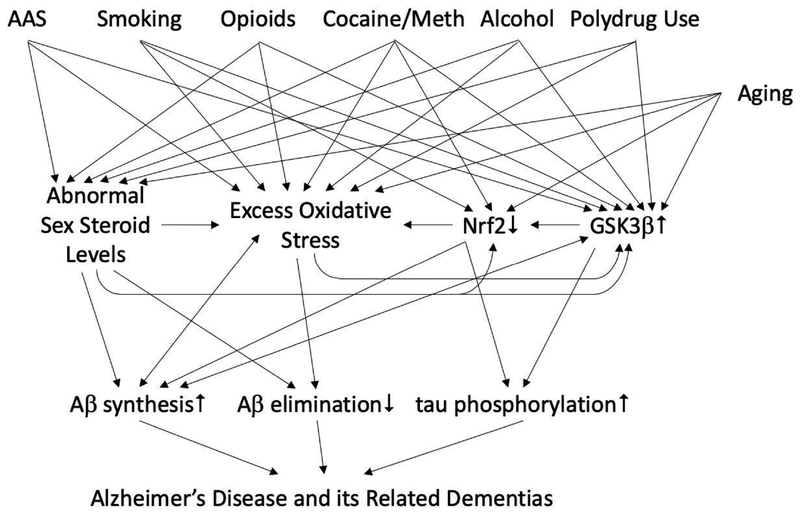
Figure 3:
Model for supraphysiologic AAS use, other substance use disorders, and biological mediators in the causation of Alzheimer’s Disease and its Related Dementias. AAS use and other substance use disorders, which develop by young adulthood, induce premature hypogonadism and/or excess oxidative stress, effects that are associated with increased Aβ and tau-P burdens in later life. Accordingly, substance use disorders may constitute early, modifiable causal factors for the development of AD/ADRD. Treatments that optimize sex steroid hormone levels, that reduce excess oxidative stress, or that inhibit GSK3β activity may exert powerful multi-targeting benefits on key mediators in the causal pathway to AD/ADRD. Legend: AAS: supraphysiologic-dose anabolicandrogenic steroid abuse; Aβ: beta-amyloid protein; AD/ADRD: Alzheimer’s Disease and its Related Dementias; GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β; Meth: methamphetamine; Nrf2: Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2.